Understanding The Periodic Table: Trends And Their Significance In 2025
Understanding the Periodic Table: Trends and Their Significance in 2025
Understanding the Periodic Table: Trends and Their Significance in 2025
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Periodic Table: Trends and Their Significance in 2025. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Periodic Table: Trends and Their Significance in 2025
/PeriodicTable-Trends-56a1310e5f9b58b7d0bcea8a.png)
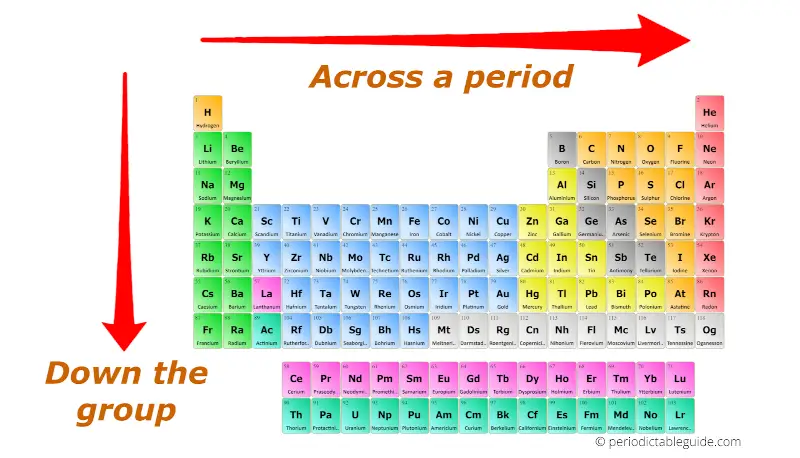
The periodic table, a cornerstone of chemistry, arranges elements based on their atomic number and recurring chemical properties. This arrangement reveals fascinating periodic trends, predictable patterns in elemental behavior that are crucial for understanding chemical reactions, predicting properties of unknown elements, and advancing scientific discovery.
Exploring the Periodic Trends:
1. Atomic Radius: The atomic radius refers to the distance from the nucleus to the outermost electron shell. Moving down a group (column) on the periodic table, atomic radius increases due to the addition of electron shells. Conversely, moving across a period (row) from left to right, atomic radius decreases because the increasing nuclear charge pulls electrons closer to the nucleus.
2. Ionization Energy: Ionization energy represents the minimum energy required to remove an electron from a gaseous atom. As you move down a group, ionization energy decreases because the outermost electron is further from the nucleus and experiences weaker attraction. Conversely, moving across a period, ionization energy increases due to the stronger attraction between the nucleus and the electrons.
3. Electron Affinity: Electron affinity describes the change in energy when an electron is added to a neutral atom in the gaseous state. Generally, electron affinity increases across a period as the increasing nuclear charge attracts additional electrons more strongly. However, down a group, electron affinity shows less predictable trends due to the increasing size of the atom.
4. Electronegativity: Electronegativity measures the tendency of an atom to attract electrons in a chemical bond. It increases across a period due to the increasing nuclear charge and decreases down a group as the outermost electrons are further from the nucleus.
5. Metallic Character: Metallic character refers to the tendency of an element to lose electrons and form positive ions. Elements with strong metallic character are typically good conductors of heat and electricity. Metallic character decreases across a period as elements become more electronegative and increases down a group as the outermost electron is further from the nucleus and easier to remove.
6. Reactivity: Reactivity refers to how readily an element participates in chemical reactions. Generally, elements with low ionization energies and high metallic character are more reactive. For example, alkali metals (Group 1) are highly reactive due to their tendency to lose one electron easily.
7. Oxidation States: Oxidation state refers to the charge an atom would have if all its bonds were ionic. The oxidation state of an element can vary depending on the other elements it bonds with. Understanding oxidation states is crucial for predicting chemical reactions and balancing equations.
8. Physical Properties: Periodic trends also influence physical properties like melting point, boiling point, and density. For instance, elements in the same group often exhibit similar melting and boiling points due to their similar interatomic forces.
The Significance of Periodic Trends in 2025:
Understanding periodic trends is essential for various fields in 2025 and beyond. These trends provide a framework for:
- Predicting Properties: Scientists can predict the properties of new elements or compounds based on their position in the periodic table. This is particularly valuable in the discovery and development of novel materials with specific applications.
- Designing Materials: Engineers and material scientists leverage periodic trends to design materials with desired properties. For example, understanding electronegativity helps in designing semiconductors with specific band gaps for electronics.
- Understanding Chemical Reactions: Periodic trends provide insights into the reactivity of elements and their tendency to form specific bonds. This knowledge is crucial for understanding and predicting chemical reactions in various contexts.
- Developing New Technologies: Periodic trends are vital for the development of advanced technologies such as batteries, catalysts, and solar cells. By understanding the properties of elements, scientists can design materials with improved performance and efficiency.
- Environmental Science: Periodic trends are essential for understanding the environmental impact of different elements. For example, understanding the reactivity of heavy metals helps in developing strategies for their safe handling and disposal.
Related Searches:
1. Periodic Table Trends and Reactivity: This search explores the relationship between periodic trends and the reactivity of elements. It delves into how factors like ionization energy, electronegativity, and metallic character influence how readily elements participate in chemical reactions.
2. Periodic Trends and Bonding: This search investigates how periodic trends influence the types of bonds elements form. It examines the relationship between electronegativity and the formation of ionic, covalent, and metallic bonds.
3. Periodic Trends and Physical Properties: This search explores the connection between periodic trends and the physical properties of elements. It examines how factors like atomic radius and metallic character affect properties like melting point, boiling point, and density.
4. Periodic Trends and Applications: This search explores the practical applications of periodic trends in various fields. It examines how understanding these trends contributes to the design of materials, the development of new technologies, and the understanding of chemical reactions.
5. Periodic Trends and the History of Chemistry: This search delves into the historical development of the periodic table and the discovery of periodic trends. It examines the contributions of key scientists like Dmitri Mendeleev and Henry Moseley.
6. Periodic Trends and the Future of Chemistry: This search explores the potential future applications of periodic trends in fields like materials science, nanotechnology, and medicine. It examines how understanding these trends can lead to the development of innovative solutions for global challenges.
7. Periodic Trends and the Environment: This search investigates the role of periodic trends in understanding the environmental impact of elements. It examines how factors like reactivity and oxidation states influence the behavior of elements in the environment.
8. Periodic Trends and Education: This search explores the importance of teaching periodic trends in chemistry education. It examines how understanding these trends can help students develop a deeper understanding of chemical principles and applications.
FAQs about Periodic Trends:
Q: What are the main periodic trends?
A: The main periodic trends include atomic radius, ionization energy, electron affinity, electronegativity, metallic character, reactivity, oxidation states, and physical properties like melting point and boiling point.
Q: Why are periodic trends important?
A: Periodic trends** are important because they provide a framework for understanding and predicting the behavior of elements. They help us understand chemical reactions, design materials, and develop new technologies.
Q: How are periodic trends related to the structure of the periodic table?
A: The periodic table is organized based on the recurring chemical properties of elements, which are directly related to periodic trends. The arrangement of elements in the table reflects the trends in atomic radius, ionization energy, and other properties.
Q: How can I learn more about periodic trends?
A: You can learn more about periodic trends by consulting chemistry textbooks, online resources, and engaging in hands-on experiments.
Tips for Understanding Periodic Trends:
- Visualize the Periodic Table: Use a periodic table as a visual aid to understand the trends. Notice how the properties of elements change as you move across periods and down groups.
- Practice with Examples: Apply your knowledge of periodic trends by working through examples and solving problems.
- Relate Trends to Real-World Applications: Understand how periodic trends are used in various fields like material science, medicine, and environmental science.
- Connect with Other Concepts: Relate periodic trends to other concepts in chemistry, such as bonding, chemical reactions, and stoichiometry.
Conclusion:
Periodic trends are fundamental concepts in chemistry that provide valuable insights into the behavior of elements. By understanding these trends, we can predict properties, design materials, and develop new technologies. As we continue to explore the world of chemistry, periodic trends will remain essential tools for scientific discovery and innovation.
.PNG)



/chart-of-periodic-table-trends-608792-v1-6ee35b80170349e8ab67865a2fdfaceb.png)

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Periodic Table: Trends and Their Significance in 2025. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!