Understanding Periodic Table Trends: A Comprehensive Guide For 2025 And Beyond
Understanding Periodic Table Trends: A Comprehensive Guide for 2025 and Beyond
Understanding Periodic Table Trends: A Comprehensive Guide for 2025 and Beyond
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Understanding Periodic Table Trends: A Comprehensive Guide for 2025 and Beyond. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Understanding Periodic Table Trends: A Comprehensive Guide for 2025 and Beyond
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Understanding Periodic Table Trends: A Comprehensive Guide for 2025 and Beyond
- 3.1 Key Periodic Table Trends
- 3.2 The Importance of Periodic Table Trends
- 3.3 Worksheet Periodic Table Trends Answers 2025
- 3.4 Related Searches
- 3.5 FAQs
- 3.6 Tips for Using Periodic Table Trends
- 3.7 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Understanding Periodic Table Trends: A Comprehensive Guide for 2025 and Beyond
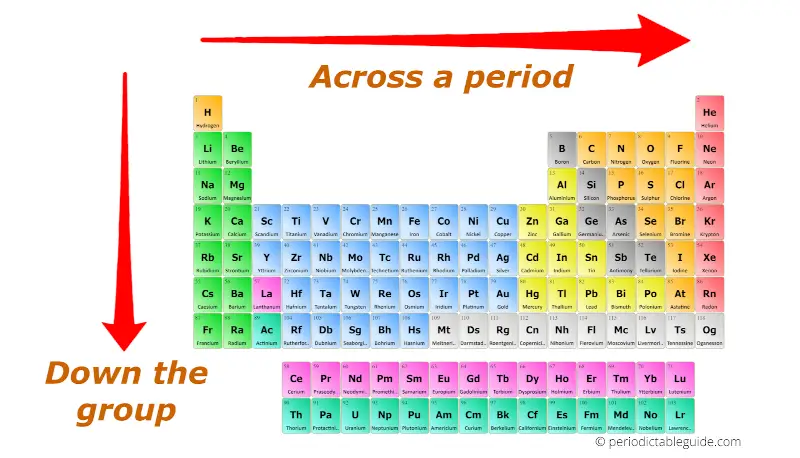
The periodic table is a fundamental tool in chemistry, organizing elements based on their atomic structure and recurring properties. Understanding the trends within this table is crucial for predicting and explaining chemical behavior, which is essential for various scientific disciplines, including materials science, medicine, and environmental studies. This guide will delve into the key trends of the periodic table, providing a comprehensive understanding for students, researchers, and anyone interested in the world of chemistry.
Key Periodic Table Trends
The periodic table reveals several fundamental trends that govern the behavior of elements. These trends arise from the arrangement of electrons within atoms, particularly the outermost shell, known as the valence shell. The valence electrons are responsible for chemical bonding and determine the reactivity of an element.
1. Atomic Radius: The atomic radius is the distance between the nucleus of an atom and its outermost electron shell. Moving down a group (vertical column) in the periodic table, the atomic radius increases. This is because the number of electron shells increases, leading to greater distances between the nucleus and the outermost electrons. Moving across a period (horizontal row) from left to right, the atomic radius generally decreases. This is due to an increase in the number of protons in the nucleus, leading to a stronger attraction between the nucleus and the electrons, pulling them closer.
2. Ionization Energy: Ionization energy is the minimum energy required to remove an electron from a gaseous atom in its ground state. The ionization energy generally increases as you move across a period from left to right. This is because the increasing nuclear charge holds the electrons more tightly, making it harder to remove an electron. However, moving down a group, the ionization energy decreases due to the increasing distance between the nucleus and the valence electrons, making them easier to remove.
3. Electron Affinity: Electron affinity is the change in energy when an electron is added to a neutral atom to form a negative ion. Generally, electron affinity increases as you move across a period from left to right. This is because the increasing nuclear charge attracts the added electron more strongly. However, moving down a group, electron affinity generally decreases because the added electron is further from the nucleus and experiences less attraction.
4. Electronegativity: Electronegativity is the ability of an atom to attract electrons in a chemical bond. It increases as you move across a period from left to right because the increasing nuclear charge attracts electrons more strongly. Moving down a group, electronegativity generally decreases because the valence electrons are further from the nucleus and experience less attraction.
5. Metallic Character: Metallic character refers to the tendency of an element to lose electrons and form positive ions (cations). Metallic character generally increases as you move down a group and decreases as you move across a period. This trend is closely related to ionization energy and electronegativity. Elements with low ionization energy and low electronegativity exhibit strong metallic character.
6. Non-Metallic Character: Non-metallic character is the tendency of an element to gain electrons and form negative ions (anions). Non-metallic character increases as you move across a period from left to right and decreases as you move down a group.
7. Reactivity: Reactivity refers to the tendency of an element to participate in chemical reactions. The reactivity of metals generally increases as you move down a group. This is because the outermost electrons are further from the nucleus and are more easily lost. However, moving across a period from left to right, the reactivity of metals decreases, while the reactivity of non-metals increases. This is because the increasing nuclear charge holds the electrons more tightly, making it harder for metals to lose electrons and easier for non-metals to gain electrons.
8. Oxidation States: Oxidation states represent the charge an atom would have if all its bonds were ionic. The most common oxidation state for an element is often related to its group number. For example, alkali metals (Group 1) typically have an oxidation state of +1, while halogens (Group 17) typically have an oxidation state of -1.
The Importance of Periodic Table Trends
Understanding the periodic table trends is essential for several reasons:
-
Predicting Chemical Properties: By knowing the trends, we can predict the chemical properties of elements without even conducting experiments. This is invaluable for understanding the behavior of substances in various applications.
-
Designing New Materials: The periodic table trends guide the development of new materials with desired properties. For example, understanding the relationship between atomic radius and conductivity helps design materials for specific electrical applications.
-
Understanding Chemical Reactions: The trends explain why certain elements react with each other and how the products of these reactions are formed. This knowledge is crucial for understanding chemical reactions and designing new chemical processes.
-
Environmental Chemistry: The periodic table trends help understand the behavior of elements in the environment, including their interactions with living organisms and their impact on ecosystems.
Worksheet Periodic Table Trends Answers 2025
Worksheet Periodic Table Trends Answers 2025 are valuable resources for students learning about the periodic table and its trends. These worksheets typically include various questions and exercises designed to test understanding and reinforce the concepts.
Here’s an example of a question from a worksheet:
"Arrange the following elements in order of increasing electronegativity: Li, F, O, Be."
Answer: Be < Li < O < F
Explanation: Electronegativity increases as you move across a period and decreases as you move down a group. Therefore, F, being in the top right corner of the periodic table, will have the highest electronegativity, followed by O, then Li, and finally Be.
Benefits of Using Worksheets:
-
Reinforce Learning: Worksheets provide a structured way to practice and reinforce the concepts learned in class.
-
Identify Gaps in Understanding: By working through worksheets, students can identify areas where they need additional clarification or practice.
-
Develop Problem-Solving Skills: Worksheets encourage students to apply their knowledge to solve problems and develop critical thinking skills.
-
Prepare for Assessments: Worksheets often mimic the format of assessments, helping students prepare for exams and quizzes.
Related Searches
1. Periodic Table Trends Worksheet Answers Key: These answers keys provide solutions to various periodic table trend worksheets, allowing students to check their work and ensure they understand the concepts correctly.
2. Periodic Table Trends Worksheet Pdf: These worksheets are readily available in PDF format, making them easy to download and print for offline use.
3. Periodic Table Trends Worksheet High School: These worksheets are specifically designed for high school students, covering the concepts in a more advanced manner.
4. Periodic Table Trends Worksheet College: These worksheets are intended for college-level students, covering the topics in greater depth and complexity.
5. Periodic Table Trends Worksheet Answers Free: These worksheets are available for free download, making them accessible to everyone.
6. Periodic Table Trends Worksheet Printable: These worksheets can be printed out for easy use, allowing students to work through them offline.
7. Periodic Table Trends Worksheet Doc: These worksheets are available in Microsoft Word format, allowing users to edit and customize them as needed.
8. Periodic Table Trends Worksheet Answers Chemistry: These worksheets are specifically focused on chemistry, providing exercises and questions related to the chemical properties of elements.
FAQs
1. What is the most important periodic table trend?
There is no single "most important" trend; each trend is crucial for understanding different aspects of chemical behavior. However, understanding the trend of electronegativity is essential for predicting bond polarity and the types of chemical reactions that will occur.
2. How can I remember the periodic table trends?
There are several mnemonic devices and tricks to help remember the trends. One common method is to use the acronym "IONIC" to represent the trends: Ionization energy, Oxidation states, Non-metallic character, Ionic radius, Chemical reactivity.
3. Why are periodic table trends important for everyday life?
Periodic table trends are essential for various aspects of everyday life. For example, understanding the reactivity of elements helps develop new materials for electronics, medicine, and construction.
4. Can I use periodic table trends to predict the properties of unknown elements?
Yes, periodic table trends can be used to predict the properties of unknown elements. By understanding the trends, we can extrapolate the properties of undiscovered elements based on their position in the periodic table.
Tips for Using Periodic Table Trends
-
Visualize the Periodic Table: Use a periodic table chart to visualize the trends and make connections between elements.
-
Practice with Examples: Work through various examples to solidify your understanding of the trends and their applications.
-
Connect Trends to Chemical Properties: Relate the trends to the chemical properties of elements, such as reactivity, bonding, and oxidation states.
-
Use Mnemonic Devices: Employ mnemonics or tricks to help remember the trends and their directions.
Conclusion
The periodic table is a powerful tool for understanding the behavior of elements and their interactions. By understanding the key trends of the periodic table, we can predict and explain chemical properties, design new materials, and advance our understanding of the natural world. Whether you are a student, researcher, or simply curious about the world around you, mastering the periodic table trends will provide you with a valuable framework for exploring the fascinating world of chemistry.
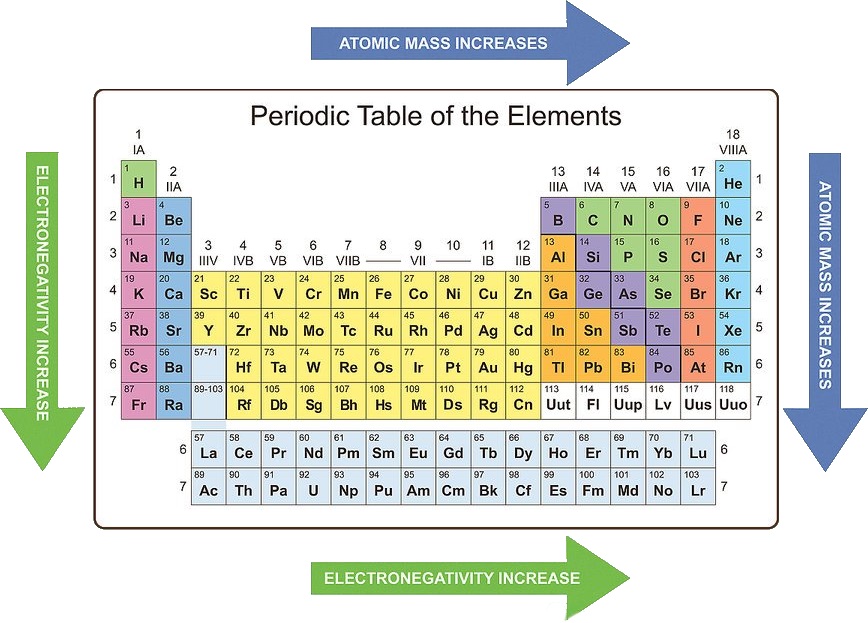
/chart-of-periodic-table-trends-608792-v1-6ee35b80170349e8ab67865a2fdfaceb.png)

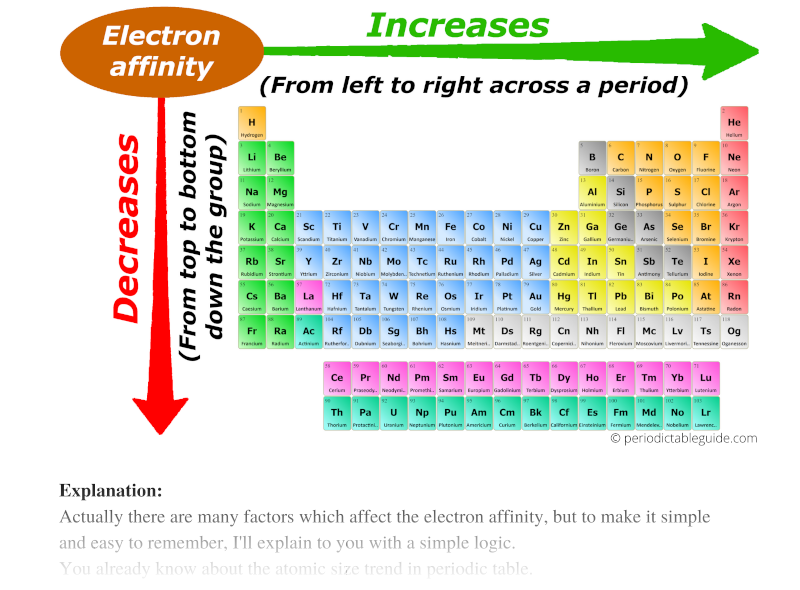
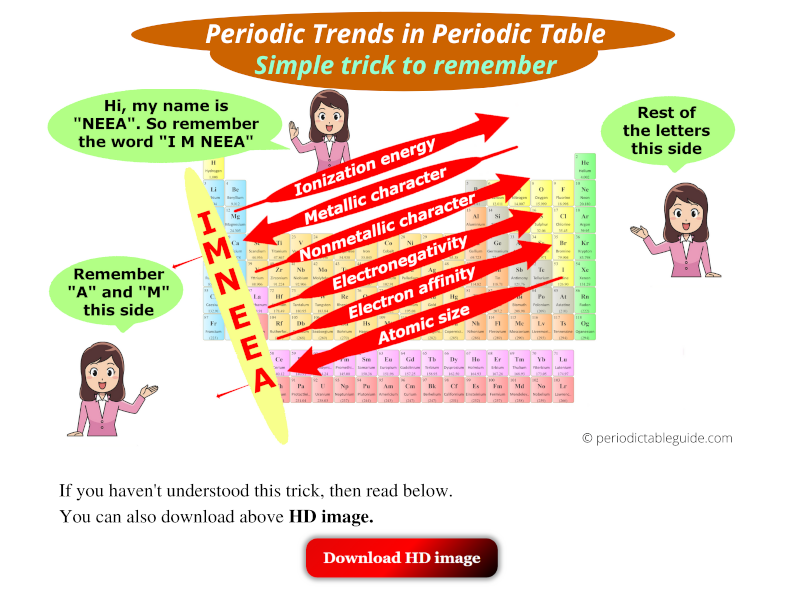
.PNG)

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding Periodic Table Trends: A Comprehensive Guide for 2025 and Beyond. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!