Navigating The Technological Landscape Of 2025: Key Trends And Their Impact
Navigating the Technological Landscape of 2025: Key Trends and Their Impact
Navigating the Technological Landscape of 2025: Key Trends and Their Impact
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Technological Landscape of 2025: Key Trends and Their Impact. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Navigating the Technological Landscape of 2025: Key Trends and Their Impact
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Navigating the Technological Landscape of 2025: Key Trends and Their Impact
- 3.1 1. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
- 3.2 2. The Metaverse and Extended Reality (XR)
- 3.3 3. Blockchain Technology and Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
- 3.4 4. Edge Computing and the Internet of Things (IoT)
- 3.5 5. Quantum Computing
- 3.6 6. 5G and Beyond
- 3.7 7. Cybersecurity and Privacy
- 3.8 8. Sustainability and Ethical Considerations
- 3.9 FAQs on Latest Technical Trends 2025
- 3.10 Tips for Embracing Latest Technical Trends 2025
- 3.11 Conclusion: Shaping the Future with Technological Advancements
- 4 Closure
Navigating the Technological Landscape of 2025: Key Trends and Their Impact

The technological landscape is constantly evolving, driven by innovation and the insatiable demand for efficiency, connectivity, and user-centric experiences. As we approach 2025, several trends are poised to reshape industries, redefine business models, and fundamentally alter how we interact with the world.
This exploration delves into the key trends shaping the technological landscape of 2025, examining their potential impact and offering insights into their implications for individuals, businesses, and society as a whole.
1. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
AI and ML are no longer futuristic concepts; they are rapidly becoming integral to everyday life. The ability of machines to learn, adapt, and make intelligent decisions based on data is transforming numerous sectors.
Applications of AI and ML:
- Personalized Experiences: AI powers personalized recommendations, tailored content, and customized services across e-commerce, entertainment, and healthcare.
- Automation and Efficiency: AI-driven automation is streamlining tasks, optimizing workflows, and freeing up human resources for higher-level activities in manufacturing, finance, and logistics.
- Predictive Analytics: AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns, predict future trends, and support strategic decision-making in areas like risk management, marketing, and healthcare.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): AI-powered NLP enables machines to understand and interpret human language, facilitating seamless interactions through chatbots, virtual assistants, and automated customer service.
- Computer Vision: AI-powered computer vision systems analyze images and videos to identify objects, interpret scenes, and automate tasks in fields like autonomous vehicles, medical imaging, and security.
Benefits of AI and ML:
- Increased Efficiency: Automation reduces manual labor, streamlines processes, and improves overall productivity.
- Enhanced Decision-Making: AI-powered analytics provide data-driven insights for informed decision-making.
- Personalized Experiences: AI enables tailored experiences, improving customer satisfaction and engagement.
- Innovation and New Opportunities: AI fuels innovation by enabling the development of new products, services, and business models.
Challenges of AI and ML:
- Ethical Concerns: AI raises ethical questions about bias, privacy, job displacement, and the potential for misuse.
- Data Security and Privacy: AI relies on vast amounts of data, raising concerns about data security and privacy.
- Transparency and Explainability: The complex nature of AI algorithms can make it challenging to understand how decisions are made, raising concerns about transparency and accountability.
2. The Metaverse and Extended Reality (XR)
The metaverse represents a persistent, shared, and immersive digital space where users can interact, work, and play. XR technologies, including virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and mixed reality (MR), create immersive experiences that blur the lines between the physical and digital worlds.
Applications of the Metaverse and XR:
- Gaming and Entertainment: The metaverse offers immersive gaming experiences, virtual concerts, and interactive entertainment.
- Social Connection: Virtual worlds provide platforms for social interaction, virtual events, and remote collaboration.
- Education and Training: XR enables immersive learning experiences, simulations, and hands-on training in various fields.
- Retail and E-commerce: Virtual showrooms and interactive product demos offer immersive shopping experiences.
- Healthcare and Wellness: XR is being used for remote patient care, virtual therapy sessions, and medical training.
Benefits of the Metaverse and XR:
- Immersive Experiences: XR technologies create engaging and immersive experiences that enhance user engagement.
- Enhanced Communication and Collaboration: Virtual worlds facilitate seamless communication and collaboration across geographical boundaries.
- New Opportunities for Innovation: The metaverse opens up new avenues for business models, content creation, and social interaction.
Challenges of the Metaverse and XR:
- Technological Maturity: The metaverse is still in its early stages of development, requiring significant technological advancements.
- Accessibility and Cost: The high cost of hardware and software can limit accessibility for some users.
- Ethical Considerations: The metaverse raises concerns about privacy, data security, and the potential for digital addiction.
3. Blockchain Technology and Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
Blockchain technology is revolutionizing the way we manage and exchange information and value. It offers a secure, transparent, and tamper-proof system for recording transactions, enabling trust and efficiency.
Applications of Blockchain Technology:
- Cryptocurrencies: Blockchain underpins cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum, offering decentralized and secure digital assets.
- Supply Chain Management: Blockchain provides transparency and traceability in supply chains, ensuring product authenticity and provenance.
- Identity Management: Blockchain can be used to create secure and verifiable digital identities, simplifying identity verification processes.
- Healthcare Records: Blockchain enables secure and tamper-proof storage and sharing of medical records, improving patient privacy and interoperability.
- Voting Systems: Blockchain can enhance election security and transparency by providing a secure and verifiable record of votes.
Benefits of Blockchain Technology:
- Security and Transparency: Blockchain offers a secure and transparent system for recording and verifying transactions.
- Decentralization: Blockchain eliminates reliance on centralized authorities, empowering users and fostering trust.
- Efficiency and Cost Reduction: Blockchain streamlines processes and reduces transaction costs.
- New Business Models: Blockchain enables innovative business models, fostering new opportunities for value creation and exchange.
Challenges of Blockchain Technology:
- Scalability: Blockchain networks can face scalability challenges as the number of transactions increases.
- Regulation and Compliance: The decentralized nature of blockchain raises regulatory and compliance challenges.
- Technical Complexity: Understanding and implementing blockchain technology can be complex.
DeFi (Decentralized Finance)
DeFi is a rapidly growing sector that leverages blockchain technology to provide financial services without reliance on traditional intermediaries.
Applications of DeFi:
- Lending and Borrowing: DeFi platforms allow users to lend and borrow cryptocurrencies without intermediaries.
- Trading and Exchange: DeFi platforms offer decentralized exchanges for trading cryptocurrencies.
- Insurance: DeFi protocols provide decentralized insurance solutions for protecting against financial risks.
- Yield Farming: DeFi platforms allow users to earn interest on their crypto assets by providing liquidity.
Benefits of DeFi:
- Financial Inclusion: DeFi makes financial services accessible to individuals who may not have access to traditional banking systems.
- Transparency and Security: DeFi platforms operate on open and transparent blockchains, enhancing security and accountability.
- Innovation and New Opportunities: DeFi is driving innovation in the financial sector, creating new products and services.
Challenges of DeFi:
- Volatility: The value of cryptocurrencies can fluctuate significantly, creating risk for DeFi users.
- Smart Contract Security: DeFi relies on smart contracts, which can be vulnerable to security breaches.
- Regulation and Compliance: The decentralized nature of DeFi presents challenges for regulation and compliance.
4. Edge Computing and the Internet of Things (IoT)
Edge computing brings computation and data storage closer to the source of data, reducing latency and enabling real-time analysis. The Internet of Things (IoT) connects physical devices to the internet, enabling data collection, analysis, and remote control.
Applications of Edge Computing and IoT:
- Smart Homes and Cities: Edge computing and IoT enable smart homes, connected devices, and smart city infrastructure.
- Industrial Automation: Edge computing and IoT optimize industrial processes, improving efficiency and productivity.
- Healthcare Monitoring: Edge computing and IoT enable remote patient monitoring, real-time data analysis, and personalized healthcare.
- Autonomous Vehicles: Edge computing and IoT are crucial for autonomous vehicles, enabling real-time decision-making and data processing.
Benefits of Edge Computing and IoT:
- Reduced Latency: Edge computing minimizes latency by processing data closer to the source.
- Enhanced Real-Time Analysis: Edge computing enables real-time data analysis, supporting faster decision-making.
- Increased Efficiency: Edge computing and IoT optimize operations, improving efficiency and productivity.
- New Opportunities for Innovation: Edge computing and IoT enable the development of innovative applications and services.
Challenges of Edge Computing and IoT:
- Security and Privacy: The proliferation of connected devices raises concerns about security and data privacy.
- Data Management and Storage: Managing and storing vast amounts of data from IoT devices presents challenges.
- Interoperability: Ensuring interoperability between different IoT devices and platforms is crucial.
5. Quantum Computing
Quantum computing harnesses the principles of quantum mechanics to perform calculations that are impossible for classical computers. This technology has the potential to revolutionize fields like drug discovery, materials science, and artificial intelligence.
Applications of Quantum Computing:
- Drug Discovery and Materials Science: Quantum computers can simulate complex molecular interactions, accelerating drug discovery and materials development.
- Financial Modeling: Quantum computing can optimize financial models and improve risk management.
- Cryptography: Quantum computing poses a threat to current encryption methods, driving the development of new quantum-resistant cryptography.
- Artificial Intelligence: Quantum computing can enhance AI algorithms, enabling more efficient and powerful machine learning models.
Benefits of Quantum Computing:
- Exponential Speedup: Quantum computers can perform certain calculations exponentially faster than classical computers.
- Solving Complex Problems: Quantum computing can tackle problems that are intractable for classical computers.
- Innovation and Breakthroughs: Quantum computing has the potential to drive innovation and breakthroughs in various fields.
Challenges of Quantum Computing:
- Technological Maturity: Quantum computing is still in its early stages of development, requiring significant technological advancements.
- Cost and Complexity: Quantum computers are expensive to build and operate, requiring specialized expertise.
- Real-World Applications: Identifying real-world applications for quantum computing is an ongoing challenge.
6. 5G and Beyond
5G is the latest generation of wireless technology, offering significantly faster speeds, lower latency, and greater capacity than previous generations.
Applications of 5G:
- Mobile Broadband: 5G enables faster download and upload speeds, supporting high-bandwidth applications like streaming, gaming, and virtual reality.
- Internet of Things (IoT): 5G facilitates the connectivity of billions of IoT devices, enabling real-time data exchange and remote control.
- Autonomous Vehicles: 5G provides the low latency and high bandwidth required for autonomous vehicles to communicate and navigate safely.
- Smart Cities and Industry 4.0: 5G supports the development of smart cities and Industry 4.0 applications, enabling real-time data analysis and control.
Benefits of 5G:
- Faster Speeds and Lower Latency: 5G offers significantly faster speeds and lower latency compared to previous generations.
- Increased Capacity: 5G supports a greater number of connected devices and data traffic.
- Enhanced Connectivity: 5G expands wireless connectivity to new areas and applications.
- New Opportunities for Innovation: 5G enables the development of new applications, services, and business models.
Challenges of 5G:
- Deployment Costs: Deploying 5G infrastructure can be expensive, requiring significant investment.
- Spectrum Availability: The availability of spectrum for 5G deployment can be limited.
- Security and Privacy: The increased connectivity and data exchange associated with 5G raise concerns about security and privacy.
Beyond 5G:
Research and development are already underway for the next generation of wireless technology, 6G. 6G is expected to offer even faster speeds, lower latency, and enhanced capabilities, enabling even more innovative applications and services.
7. Cybersecurity and Privacy
As technology advances, the threat landscape for cybersecurity and privacy is also evolving.
Cybersecurity Challenges:
- Sophisticated Cyberattacks: Cybercriminals are increasingly using sophisticated techniques, such as ransomware, phishing, and social engineering, to target individuals and organizations.
- Data Breaches: Data breaches are becoming more frequent and costly, exposing sensitive information and disrupting operations.
- Emerging Threats: New technologies, like AI and IoT, introduce new cybersecurity challenges and vulnerabilities.
Privacy Concerns:
- Data Collection and Surveillance: The increasing collection and use of personal data raise concerns about privacy and surveillance.
- Data Sharing and Consent: The sharing of personal data across platforms and organizations requires clear consent and transparency.
- Regulation and Compliance: Governments and organizations are implementing new regulations to protect privacy and data security.
Cybersecurity and Privacy Best Practices:
- Strong Passwords and Multi-Factor Authentication: Using strong passwords and multi-factor authentication helps protect accounts from unauthorized access.
- Software Updates and Security Patches: Regularly updating software and applying security patches helps mitigate vulnerabilities.
- Data Encryption: Encrypting sensitive data protects it from unauthorized access even if it is compromised.
- Data Minimization and Privacy-Preserving Technologies: Limiting the collection and use of personal data and implementing privacy-preserving technologies can enhance privacy.
8. Sustainability and Ethical Considerations
Technological advancements have a significant impact on the environment and society.
Sustainability Challenges:
- Energy Consumption: The increasing use of technology, particularly data centers and cloud computing, requires significant energy consumption.
- E-Waste: The rapid obsolescence of electronic devices generates a growing problem of e-waste.
- Environmental Impact: The manufacturing and disposal of electronic devices can have a negative impact on the environment.
Ethical Considerations:
- Algorithmic Bias: AI algorithms can perpetuate and amplify existing biases, leading to unfair or discriminatory outcomes.
- Job Displacement: Automation and AI can lead to job displacement, raising concerns about economic inequality.
- Privacy and Surveillance: The use of technology for surveillance and data collection raises ethical concerns about privacy and individual rights.
Sustainable and Ethical Practices:
- Energy-Efficient Technologies: Developing and using energy-efficient technologies can reduce energy consumption and carbon emissions.
- Responsible Disposal and Recycling: Promoting responsible e-waste disposal and recycling can minimize environmental impact.
- Ethical AI Development: Developing AI algorithms that are fair, transparent, and accountable can mitigate ethical concerns.
FAQs on Latest Technical Trends 2025
Q: What are the key benefits of AI and ML in the future?
A: AI and ML offer numerous benefits, including increased efficiency through automation, enhanced decision-making through data-driven insights, personalized experiences for improved customer satisfaction, and the creation of new products, services, and business models.
Q: How will the metaverse impact our lives?
A: The metaverse has the potential to revolutionize how we work, play, and interact socially. It offers immersive experiences, enhanced communication and collaboration, and new opportunities for innovation in fields like gaming, education, and healthcare.
Q: What are the potential risks associated with blockchain technology?
A: While blockchain offers significant benefits, it also presents challenges such as scalability, regulation, and technical complexity. Ensuring secure smart contracts and managing the volatility of cryptocurrencies are also crucial considerations.
Q: How does edge computing improve IoT applications?
A: Edge computing brings computation and data storage closer to IoT devices, reducing latency and enabling real-time data analysis. This enhances the efficiency and responsiveness of IoT applications in fields like smart homes, industrial automation, and healthcare monitoring.
Q: What are the main challenges of quantum computing?
A: Quantum computing is still in its early stages of development, facing challenges such as technological maturity, cost and complexity, and the identification of real-world applications. Overcoming these challenges is crucial for realizing the full potential of this transformative technology.
Q: How does 5G technology benefit businesses?
A: 5G enables faster speeds, lower latency, and increased capacity, empowering businesses to adopt new technologies, improve operational efficiency, and create innovative products and services. It supports applications like mobile broadband, IoT, autonomous vehicles, and smart city infrastructure.
Q: What steps can be taken to ensure cybersecurity and privacy in the digital age?
A: Strong passwords, multi-factor authentication, regular software updates, data encryption, and privacy-preserving technologies are essential for safeguarding against cyber threats and protecting personal data.
Q: How can technology be made more sustainable and ethical?
A: Promoting energy-efficient technologies, responsible e-waste disposal, and ethical AI development are crucial for mitigating the environmental and social impacts of technology. Addressing algorithmic bias, job displacement, and privacy concerns is also essential for ensuring the responsible and equitable use of technology.
Tips for Embracing Latest Technical Trends 2025
- Stay Informed: Continuously update your knowledge about emerging technologies and their implications.
- Embrace Lifelong Learning: Invest in continuous learning and development to acquire the skills needed for the future workforce.
- Experiment and Innovate: Be open to exploring new technologies and experimenting with innovative solutions.
- Collaborate and Network: Engage with others in the tech industry to share knowledge and learn from different perspectives.
- Consider Ethical Implications: Be mindful of the ethical implications of technology and strive to use it responsibly.
Conclusion: Shaping the Future with Technological Advancements
The technological trends shaping 2025 offer immense opportunities for innovation, efficiency, and improved quality of life. From AI and ML to the metaverse and quantum computing, these advancements are transforming industries, creating new business models, and redefining how we interact with the world.
However, it is crucial to approach these trends with a balance of optimism and caution. Addressing ethical considerations, ensuring cybersecurity and privacy, and promoting sustainability are essential for harnessing the full potential of these technologies while mitigating potential risks. By embracing these trends responsibly and strategically, we can shape a future where technology empowers individuals, enhances society, and drives progress for the benefit of all.
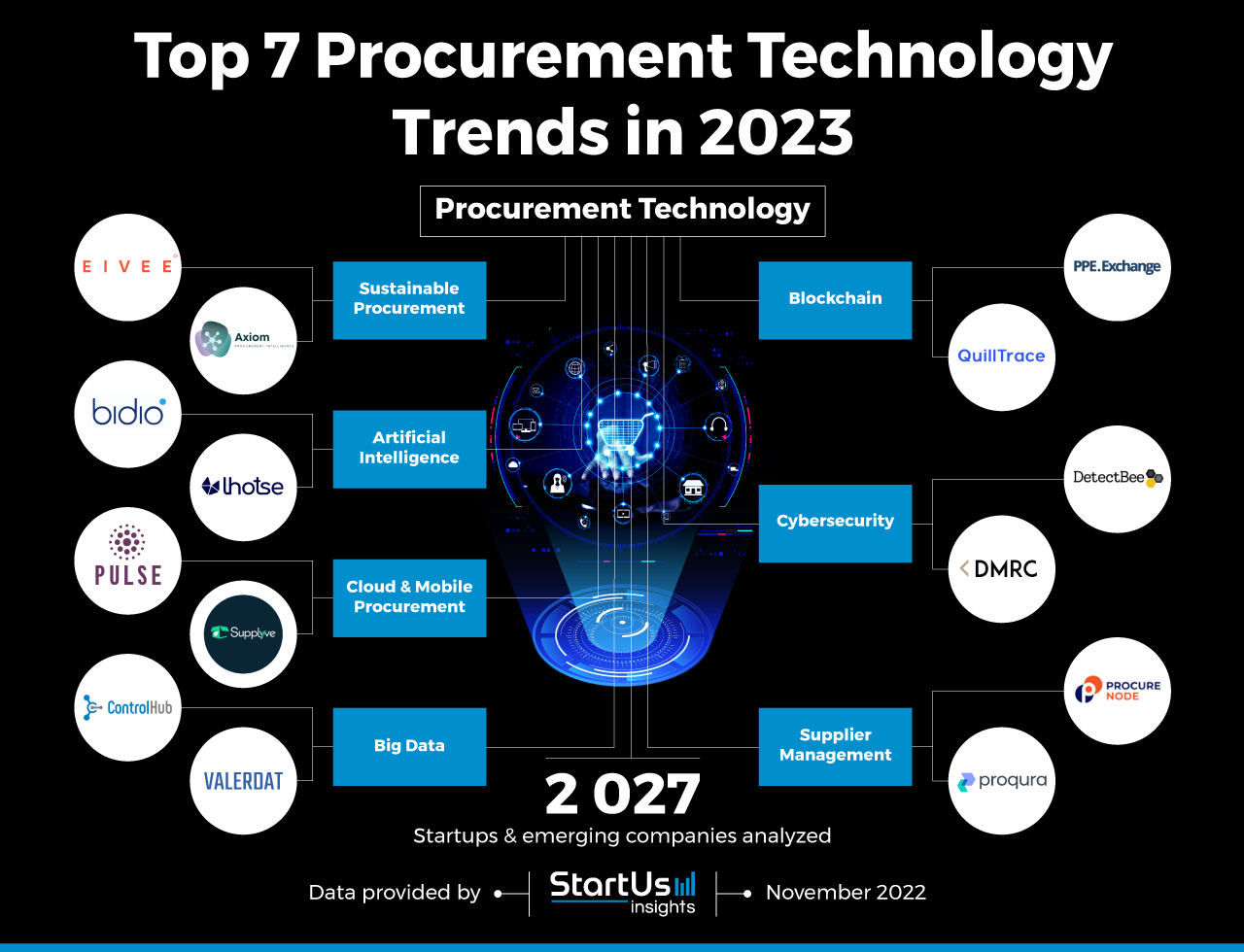

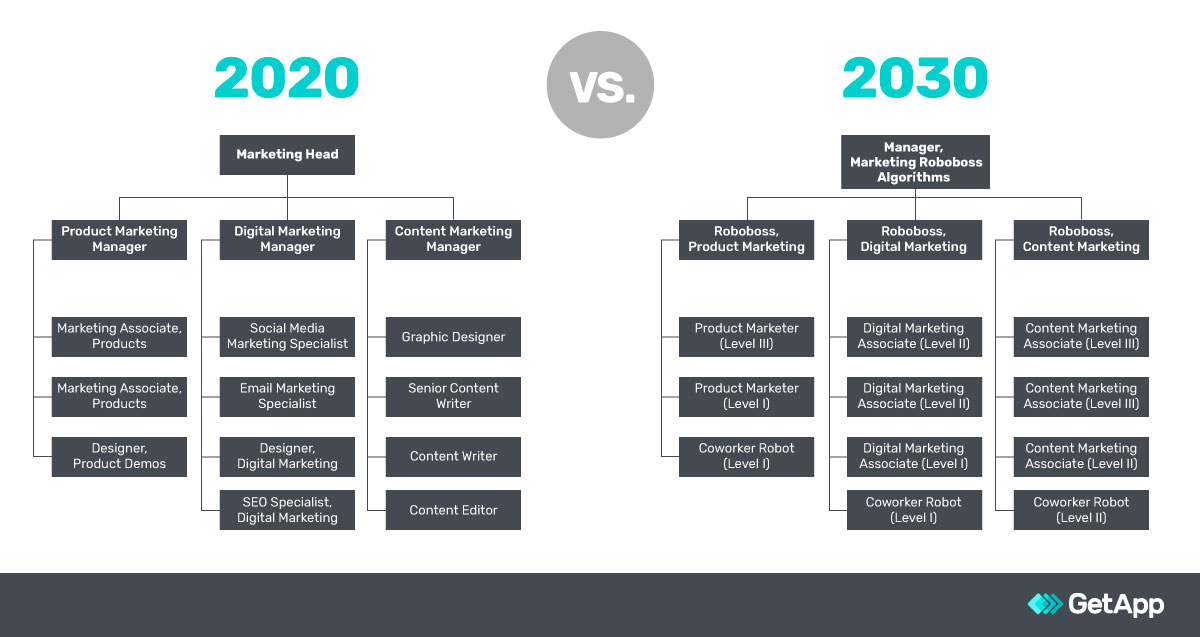

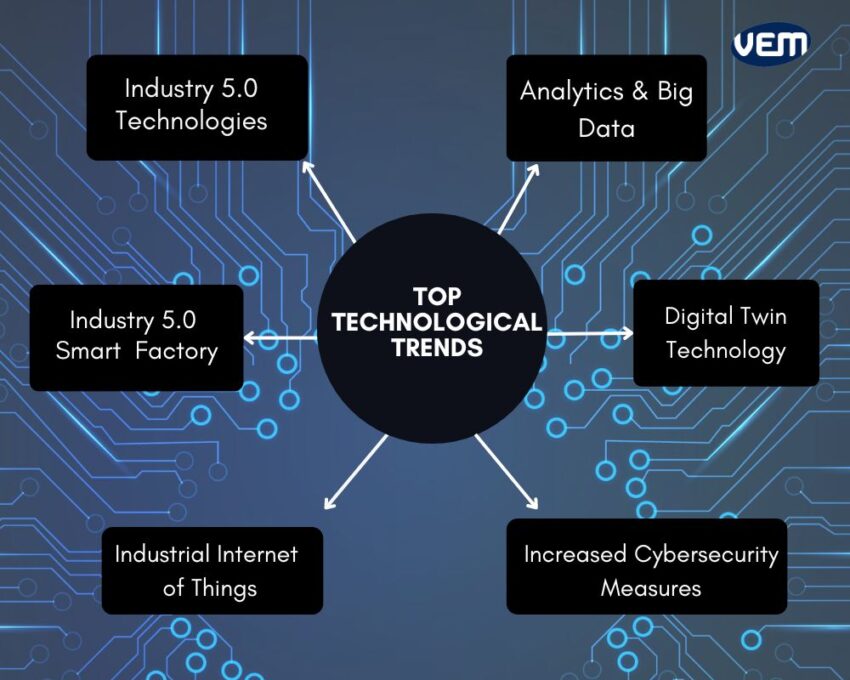

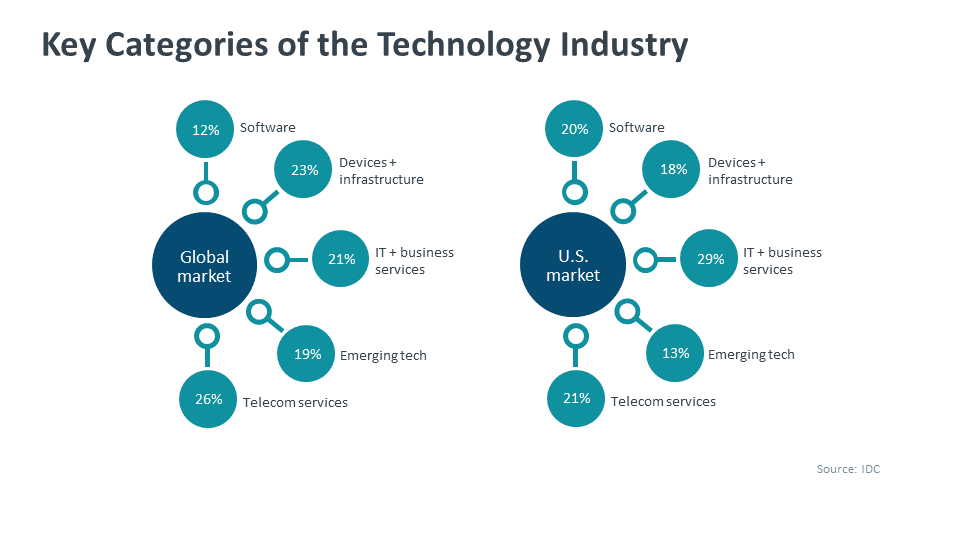

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Technological Landscape of 2025: Key Trends and Their Impact. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!