Navigating The Periodic Table: Understanding Trends And Their Applications
Navigating the Periodic Table: Understanding Trends and Their Applications
Navigating the Periodic Table: Understanding Trends and Their Applications
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Periodic Table: Understanding Trends and Their Applications. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Navigating the Periodic Table: Understanding Trends and Their Applications
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Navigating the Periodic Table: Understanding Trends and Their Applications
- 3.1 Periodic Table Trends: A Foundation for Chemical Understanding
- 3.2 The Periodic Table: A Guide to Material Design
- 3.3 Understanding the Periodic Table: A Key to Innovation
- 3.4 Related Searches
- 3.5 FAQs
- 3.6 Tips
- 3.7 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Navigating the Periodic Table: Understanding Trends and Their Applications

The periodic table is a fundamental tool in chemistry, organizing elements based on their atomic structure and resulting properties. Understanding the trends within this table is crucial for predicting chemical behavior and designing new materials. This exploration delves into the key trends and their applications, providing a comprehensive understanding of the periodic table’s structure and its significance in various fields.
Periodic Table Trends: A Foundation for Chemical Understanding
The periodic table is arranged in rows (periods) and columns (groups), with elements in the same group sharing similar chemical properties. This organization is not arbitrary; it reflects the underlying structure of atoms.
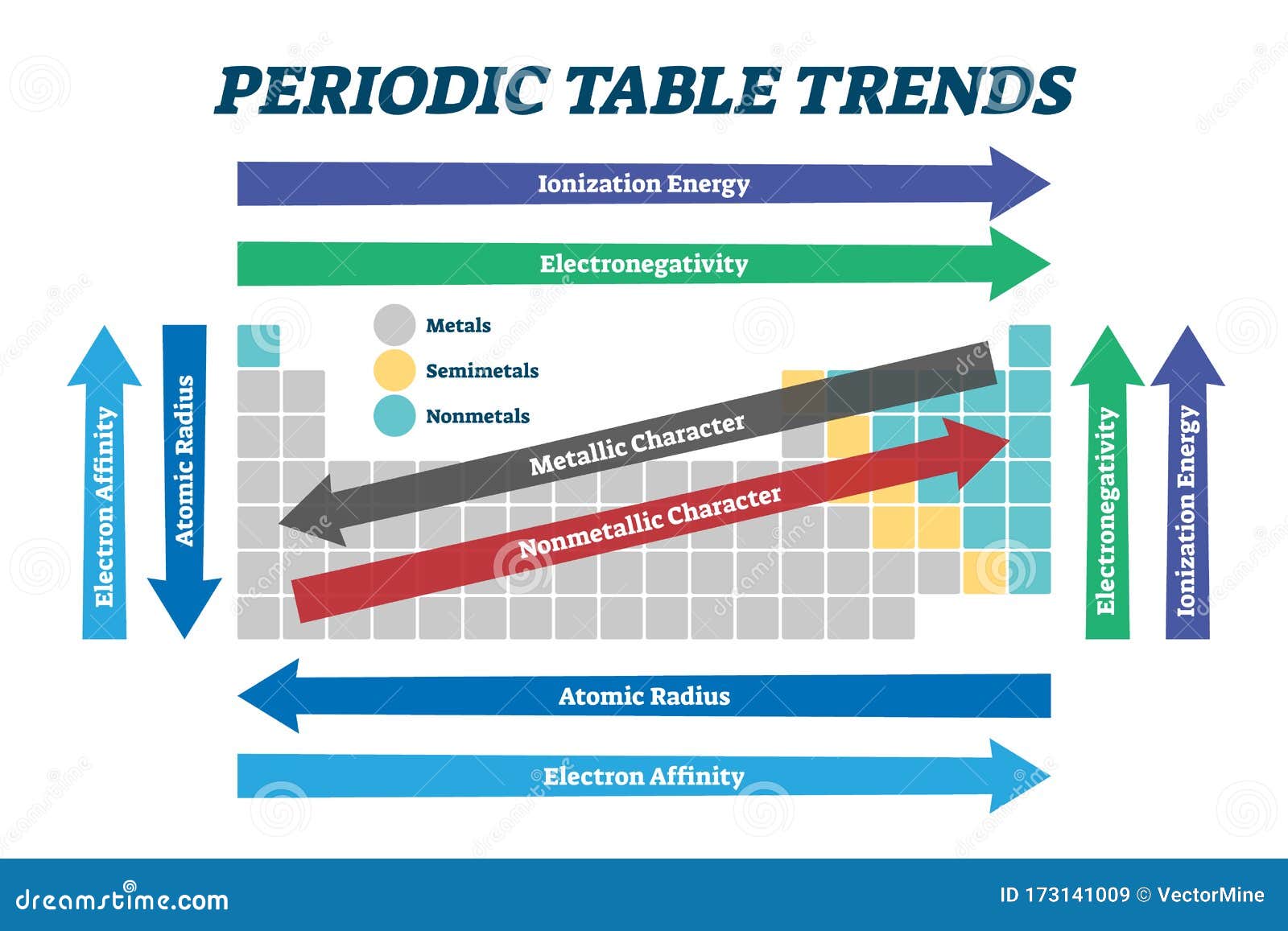
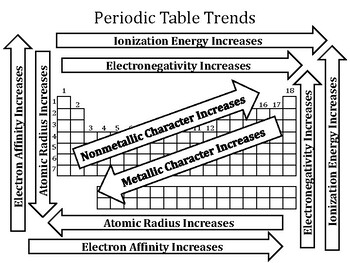
Key Trends in the Periodic Table
- Atomic Radius: Atomic radius refers to the distance between the nucleus and the outermost electron shell of an atom. Moving down a group, atomic radius increases due to the addition of electron shells. Moving across a period, atomic radius decreases due to increasing nuclear charge attracting electrons more strongly.
- Ionization Energy: Ionization energy is the minimum energy required to remove an electron from a gaseous atom in its ground state. Ionization energy generally increases across a period due to the increased nuclear charge pulling electrons closer. It decreases down a group due to the increasing distance between the nucleus and the valence electrons.
- Electron Affinity: Electron affinity is the change in energy when an electron is added to a neutral atom in its gaseous state. Generally, electron affinity increases across a period due to the increasing nuclear charge attracting incoming electrons. It decreases down a group due to the increasing distance between the nucleus and the valence electrons.
- Electronegativity: Electronegativity measures an atom’s ability to attract electrons in a chemical bond. Electronegativity generally increases across a period due to the increasing nuclear charge. It decreases down a group due to the increasing distance between the nucleus and the valence electrons.
- Metallic Character: Metallic character describes an element’s tendency to lose electrons and form cations. Metallic character increases down a group due to the decreasing ionization energy. It decreases across a period due to the increasing ionization energy.
The Periodic Table: A Guide to Material Design
The trends within the periodic table are not just theoretical concepts; they have real-world applications in various fields.
- Material Science: Understanding the trends in atomic size, ionization energy, and electronegativity allows scientists to predict the properties of materials. For example, the high electronegativity of halogens makes them excellent candidates for use in polymers and pharmaceuticals.
- Chemistry: The periodic table helps predict the reactivity of elements. Elements with low ionization energies tend to be highly reactive metals, while elements with high ionization energies are less reactive nonmetals.
- Nanotechnology: The periodic table guides the development of nanomaterials with specific properties. For example, the high surface area of nanoparticles of noble metals like gold and silver makes them ideal catalysts.
- Environmental Science: Understanding the periodic table helps scientists assess the environmental impact of various elements and compounds. For example, the high reactivity of alkali metals makes them potential pollutants.
Understanding the Periodic Table: A Key to Innovation
The periodic table is not just a static chart; it is a dynamic tool that allows scientists to understand and predict the behavior of matter. The trends within this table provide a framework for designing new materials, developing new technologies, and addressing environmental challenges.
Related Searches
1. Periodic Table Trends Worksheet
- Purpose: Periodic table trends worksheets provide a structured approach to learning and applying the periodic table trends. They typically include questions and exercises that require students to identify patterns and apply their knowledge to specific examples.
- Benefits: Worksheets help solidify understanding, identify areas of weakness, and provide practice in applying the concepts to real-world scenarios.
- Examples: Online resources and textbooks offer various periodic table trends worksheets covering different levels of difficulty.
2. Periodic Table Trends Quiz
- Purpose: Periodic table trends quizzes assess understanding of the key trends and their applications. They can be used for self-assessment or formal evaluation.
- Benefits: Quizzes provide feedback on learning progress and highlight areas requiring further study.
- Examples: Online platforms and educational websites offer interactive quizzes on periodic table trends.
3. Periodic Table Trends Chart
- Purpose: A periodic table trends chart visually summarizes the key trends across periods and groups. It serves as a reference tool for studying and understanding the relationships between elements.
- Benefits: Visual representation helps with memorization and understanding the relationships between properties and atomic structure.
- Examples: Textbooks, online resources, and classroom presentations often feature periodic table trends charts.
4. Periodic Table Trends PowerPoint
- Purpose: PowerPoint presentations provide a dynamic and engaging way to teach and explain periodic table trends. They can include visuals, animations, and interactive elements.
- Benefits: PowerPoint presentations offer a structured and visually appealing way to convey complex concepts.
- Examples: Educational institutions and online platforms offer PowerPoint presentations on periodic table trends.
5. Periodic Table Trends Practice Problems
- Purpose: Practice problems provide opportunities to apply knowledge of periodic table trends to specific scenarios. They can range from simple calculations to complex analysis.
- Benefits: Practice problems help develop problem-solving skills and reinforce understanding of the concepts.
- Examples: Textbooks, online resources, and worksheets offer various practice problems on periodic table trends.
6. Periodic Table Trends and Chemical Bonding
- Purpose: Exploring the relationship between periodic table trends and chemical bonding helps understand how the properties of elements influence the formation of molecules.
- Benefits: This connection allows prediction of bond types and the properties of compounds based on the elements involved.
- Examples: Textbooks, online resources, and classroom discussions delve into the relationship between periodic table trends and chemical bonding.
7. Periodic Table Trends and Chemical Reactions
- Purpose: Understanding the influence of periodic table trends on chemical reactions allows prediction of reactivity and product formation.
- Benefits: This knowledge is crucial for designing and understanding chemical processes.
- Examples: Textbooks, online resources, and research papers explore the impact of periodic table trends on chemical reactions.
8. Periodic Table Trends and the History of Chemistry
- Purpose: Exploring the historical development of the periodic table and the discovery of its trends provides context and understanding of how scientific knowledge evolves.
- Benefits: Learning the historical aspects highlights the importance of observation, experimentation, and collaboration in scientific discovery.
- Examples: Textbooks, online resources, and historical articles provide insights into the historical development of the periodic table.
FAQs
1. What are the main trends in the periodic table?
The main trends include atomic radius, ionization energy, electron affinity, electronegativity, and metallic character. These trends are related to the atomic structure of elements, specifically the number of protons and electrons and the arrangement of electrons in shells.
2. How do these trends affect chemical properties?
The trends influence how elements interact with each other and form chemical bonds. For example, elements with low ionization energies readily lose electrons and form cations, while elements with high electronegativity tend to gain electrons and form anions.
3. How can the periodic table be used to predict the properties of elements?
By understanding the trends, we can predict the behavior of elements within a group or period. For example, elements in the same group share similar chemical properties due to their similar electron configurations.
4. How are periodic table trends applied in real-world applications?
Periodic table trends are crucial in material science, chemistry, nanotechnology, and environmental science. They guide the design of new materials with specific properties, predict the reactivity of elements, and inform our understanding of the environmental impact of various compounds.
5. What are some resources for learning about periodic table trends?
Textbooks, online resources, educational videos, and interactive simulations offer comprehensive learning materials on periodic table trends.
Tips
- Visualize the trends: Use visual aids like charts and diagrams to understand the relationships between properties and atomic structure.
- Practice problem-solving: Work through practice problems to apply your knowledge and develop problem-solving skills.
- Connect trends to real-world applications: Explore how the trends are used in different fields to solidify your understanding.
- Use online resources: Utilize interactive simulations, quizzes, and videos to enhance your learning experience.
Conclusion
The periodic table is a powerful tool that provides a framework for understanding the behavior of elements and predicting their properties. Understanding the trends within this table is essential for various fields, from material science and chemistry to nanotechnology and environmental science. By exploring these trends and their applications, we can unlock the potential of the periodic table to drive innovation and address global challenges.
/periodictrendstable-5c4a46614cedfd000187c5db.jpg)
/chart-of-periodic-table-trends-608792-v1-6ee35b80170349e8ab67865a2fdfaceb.png)

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Periodic Table: Understanding Trends and Their Applications. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
.PNG)
