Navigating The Evolving Landscape: Cybersecurity Trends For 2025-2026
Navigating the Evolving Landscape: Cybersecurity Trends for 2025-2026
Navigating the Evolving Landscape: Cybersecurity Trends for 2025-2026
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Evolving Landscape: Cybersecurity Trends for 2025-2026. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Evolving Landscape: Cybersecurity Trends for 2025-2026
The digital landscape is in constant flux, and with it, the threats to our online security evolve at an alarming pace. As we approach 2025 and beyond, understanding the emerging cybersecurity trends is paramount for individuals, businesses, and governments alike. These trends will shape the future of digital security, influencing how we protect our data, systems, and networks.
1. The Rise of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Cybersecurity
AI is no longer a futuristic concept; it is rapidly becoming a crucial tool in the cybersecurity arsenal. Its ability to analyze vast amounts of data, identify patterns, and predict threats in real-time makes it a powerful ally in the fight against cyberattacks.
Here’s how AI is changing the game:
- Threat Detection and Prevention: AI-powered security solutions can analyze network traffic, identify suspicious activities, and proactively block potential threats before they cause harm. This includes detecting zero-day exploits, identifying malware, and recognizing phishing attempts.
- Automated Security Operations: AI can automate repetitive tasks like vulnerability scanning, log analysis, and incident response, freeing up human analysts to focus on more complex and strategic issues.
- Improved Security Posture: AI can analyze security data to identify weaknesses and vulnerabilities in systems and networks, enabling organizations to prioritize patching and remediation efforts.
2. The Growing Threat of Sophisticated Cyberattacks
As cybercriminals become more sophisticated, their attacks become more targeted, complex, and evasive.
The following trends highlight the evolving threat landscape:
- Ransomware Attacks: Ransomware continues to be a major threat, with attackers targeting critical infrastructure, healthcare, and financial institutions. These attacks often involve data encryption and extortion demands, causing significant disruption and financial losses.
- Supply Chain Attacks: Attackers are increasingly targeting software supply chains, compromising software development tools and libraries to inject malicious code into widely used applications. This allows them to gain access to a vast number of systems and networks.
- Nation-State Sponsored Attacks: State-sponsored actors are actively engaging in cyberespionage, data theft, and sabotage, targeting governments, businesses, and critical infrastructure. These attacks often involve highly sophisticated tools and techniques, making them difficult to detect and defend against.
3. The Expanding Attack Surface
The increasing reliance on cloud computing, mobile devices, and the Internet of Things (IoT) has significantly expanded the attack surface, creating new opportunities for cybercriminals.
Here’s how the attack surface is expanding:
- Cloud Computing: Cloud environments offer a vast array of interconnected services, making them attractive targets for attackers. Misconfigured cloud services, insecure APIs, and vulnerabilities in cloud infrastructure can all provide entry points for cyberattacks.
- Mobile Devices: Smartphones, tablets, and other mobile devices are becoming increasingly powerful and interconnected, making them prime targets for malware and data theft.
- IoT Devices: The proliferation of IoT devices, from smart home appliances to industrial control systems, creates a vast network of interconnected devices that are often poorly secured. This vulnerability makes them easy targets for attackers who can gain access to sensitive data or disrupt critical operations.
4. The Rise of Quantum Computing and Its Impact on Cybersecurity
Quantum computing is a revolutionary technology with the potential to transform various industries, including cybersecurity. However, it also poses significant threats to existing cryptographic methods.
Here’s how quantum computing impacts cybersecurity:
- Breaking Encryption: Quantum computers have the potential to break traditional encryption algorithms, making current security measures obsolete. This could compromise sensitive data, disrupt financial transactions, and undermine national security.
- New Cryptographic Algorithms: The development of new, quantum-resistant cryptographic algorithms is crucial to ensure the security of data and systems in the quantum era.
- Post-Quantum Cryptography: Research and development efforts are underway to create new cryptographic algorithms that are resistant to attacks by quantum computers. These algorithms will be essential for securing data in the future.
5. The Importance of Cybersecurity Education and Training
As cyberattacks become more sophisticated, it is crucial to invest in cybersecurity education and training to equip individuals and organizations with the knowledge and skills needed to protect themselves.
Here’s why cybersecurity education is vital:
- Building a Skilled Workforce: Organizations need a skilled cybersecurity workforce to implement and maintain effective security measures. This requires investing in training programs that develop the necessary skills and knowledge.
- Raising Awareness: Cybersecurity education is essential for raising awareness about online threats and promoting best practices for online safety. This includes teaching individuals how to recognize phishing attempts, protect their passwords, and avoid malicious websites.
- Developing a Culture of Security: A strong cybersecurity culture is essential for building a robust defense against cyberattacks. This involves promoting a shared understanding of security risks, encouraging responsible online behavior, and fostering collaboration between different departments.
6. The Growing Role of Government Regulations and Standards
Governments around the world are increasingly recognizing the importance of cybersecurity and enacting regulations and standards to protect individuals, businesses, and critical infrastructure.
Here’s how government regulations are shaping cybersecurity:
- Data Protection Laws: Regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) require organizations to implement strong security measures to protect personal data.
- Critical Infrastructure Security: Governments are focusing on securing critical infrastructure, such as power grids, transportation systems, and financial institutions, from cyberattacks.
- Cybersecurity Frameworks: Governments are developing cybersecurity frameworks and standards to provide guidance for organizations on best practices for security.
7. The Importance of Collaboration and Information Sharing
Collaboration and information sharing are crucial for effectively combating cyberattacks. Sharing threat intelligence, best practices, and lessons learned can help organizations stay ahead of emerging threats.
Here’s why collaboration is crucial:
- Threat Intelligence Sharing: Sharing threat intelligence, including information about known vulnerabilities, attack patterns, and indicators of compromise, can help organizations detect and respond to threats more effectively.
- Best Practices Sharing: Sharing best practices for security implementation, incident response, and vulnerability management can help organizations improve their overall security posture.
- Building a Collective Defense: Collaboration and information sharing can help organizations build a collective defense against cyberattacks, making it more difficult for attackers to succeed.
8. The Future of Cybersecurity: A Focus on Proactive Security and Resilience
The future of cybersecurity is moving away from reactive measures and towards a more proactive approach, focusing on building resilience and preventing attacks before they happen.
Here’s how proactive security is shaping the future:
- Zero Trust Security: Zero trust security models assume that no user or device can be trusted by default. This approach involves verifying every request and enforcing access controls based on strict policies.
- Threat Hunting: Threat hunting involves proactively searching for malicious activity in networks and systems, even if there are no immediate signs of compromise.
- Security Automation: Automating security tasks, such as vulnerability scanning, patch management, and incident response, can help organizations improve their efficiency and effectiveness.
Related Searches:
- Cybersecurity trends 2025: This search query explores the latest cybersecurity trends expected to emerge in 2025, highlighting the evolving threat landscape, emerging technologies, and best practices for mitigating risks.
- Cybersecurity trends 2026: Similar to the previous query, this focuses on the cybersecurity trends anticipated in 2026, emphasizing the impact of AI, quantum computing, and the increasing reliance on cloud computing.
- Cybersecurity predictions 2025: This search explores expert predictions for the future of cybersecurity in 2025, including potential threats, technological advancements, and the evolving role of cybersecurity professionals.
- Top cybersecurity threats 2025: This query delves into the most significant cybersecurity threats expected in 2025, such as ransomware, supply chain attacks, and nation-state sponsored cyberespionage.
- Cybersecurity challenges 2025: This search focuses on the challenges organizations will face in securing their systems and data in 2025, including the expanding attack surface, the rise of sophisticated cyberattacks, and the need for a skilled cybersecurity workforce.
- Cybersecurity solutions 2025: This query explores the latest cybersecurity solutions available to organizations in 2025, including AI-powered security platforms, zero trust security models, and advanced threat hunting techniques.
- Cybersecurity best practices 2025: This search delves into the best practices organizations should adopt to improve their cybersecurity posture in 2025, including implementing strong passwords, using multi-factor authentication, and regularly updating software.
- Cybersecurity career outlook 2025: This query explores the career opportunities in cybersecurity in 2025, highlighting the growing demand for skilled cybersecurity professionals and the range of career paths available.
FAQs:
1. What are the biggest cybersecurity threats in 2025-2026?
The biggest cybersecurity threats in 2025-2026 will likely include sophisticated ransomware attacks, supply chain attacks, nation-state sponsored cyberespionage, and the growing threat of quantum computing.
2. How can organizations prepare for the evolving threat landscape?
Organizations can prepare by investing in AI-powered security solutions, implementing zero trust security models, prioritizing cybersecurity education and training, and collaborating with other organizations to share threat intelligence.
3. What is the impact of quantum computing on cybersecurity?
Quantum computing poses a significant threat to existing encryption methods, making it crucial to develop new quantum-resistant algorithms and adopt post-quantum cryptography.
4. What is the role of government regulations in cybersecurity?
Government regulations are playing an increasingly important role in shaping cybersecurity, driving organizations to implement strong security measures to protect data, secure critical infrastructure, and comply with data protection laws.
5. How can individuals protect themselves from cyberattacks?
Individuals can protect themselves by using strong passwords, enabling multi-factor authentication, being cautious of phishing attempts, avoiding malicious websites, and keeping their software up-to-date.
Tips:
- Implement a Zero Trust Security Model: This approach assumes that no user or device can be trusted by default, requiring strict verification and access control measures.
- Invest in AI-Powered Security Solutions: AI can help organizations detect threats, automate security tasks, and improve their overall security posture.
- Prioritize Cybersecurity Education and Training: Equip employees with the knowledge and skills needed to recognize and respond to cyber threats.
- Collaborate and Share Threat Intelligence: Sharing information with other organizations can help build a collective defense against cyberattacks.
- Stay Informed about Emerging Threats: Keep up-to-date on the latest cybersecurity trends, vulnerabilities, and attack techniques.
Conclusion:
The cybersecurity landscape is constantly evolving, and the threats we face are becoming increasingly sophisticated. Organizations and individuals must stay informed about the latest trends, adopt proactive security measures, and invest in education and training to build a robust defense against cyberattacks. As we move into 2025 and beyond, a strong focus on security awareness, collaboration, and the adoption of new technologies will be essential for navigating the evolving digital landscape. By understanding and adapting to these cybersecurity trends, we can create a more secure and resilient online environment for all.





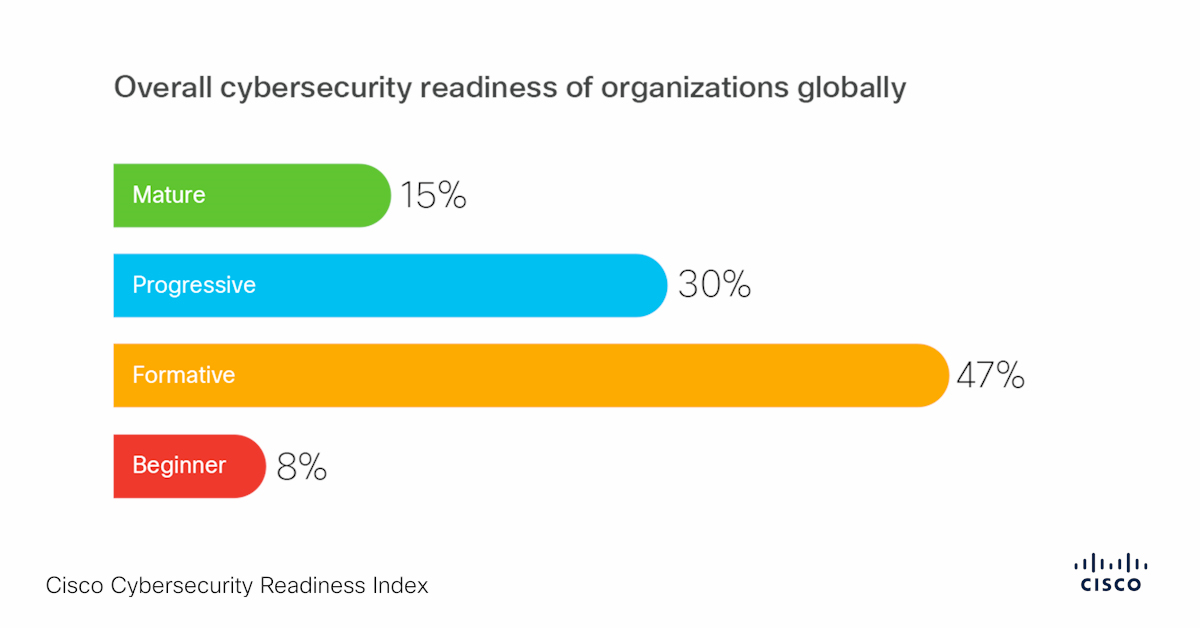


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Evolving Landscape: Cybersecurity Trends for 2025-2026. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!