Cancer Trends 2025: A Glimpse Into The Future Of Cancer Care
Cancer Trends 2025: A Glimpse into the Future of Cancer Care
Cancer Trends 2025: A Glimpse into the Future of Cancer Care
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Cancer Trends 2025: A Glimpse into the Future of Cancer Care. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Cancer Trends 2025: A Glimpse into the Future of Cancer Care
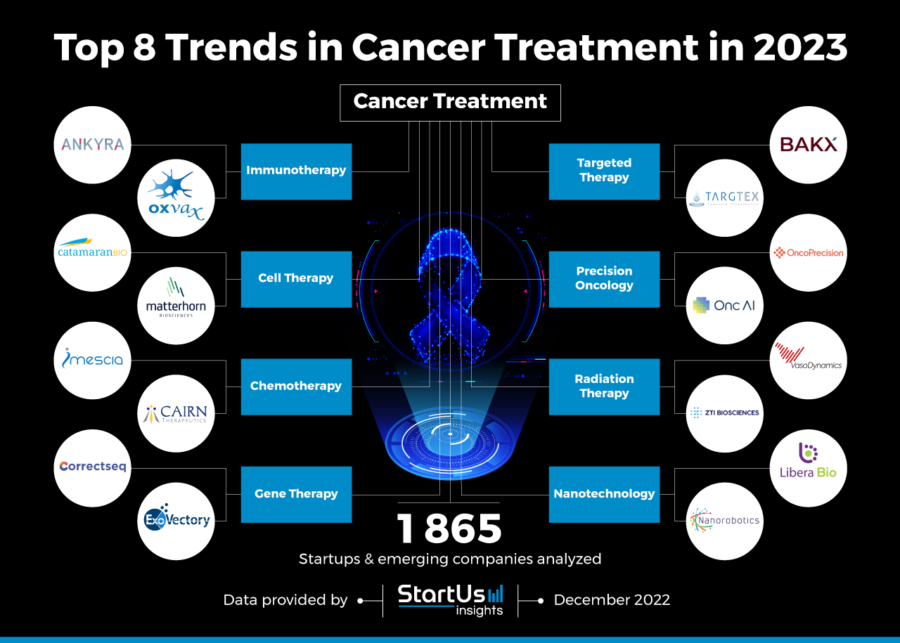
Cancer remains a formidable global health challenge, impacting millions of lives annually. However, the landscape of cancer research and treatment is rapidly evolving, driven by advancements in technology, scientific understanding, and a growing commitment to personalized medicine. This article delves into the anticipated cancer trends 2025, exploring the potential impact of these developments on cancer prevention, diagnosis, treatment, and patient outcomes.
Understanding the Trajectory of Cancer
Predicting cancer trends is a complex endeavor, influenced by a multitude of factors including demographics, lifestyle choices, environmental exposures, and access to healthcare. However, by analyzing current trends and emerging research, we can gain valuable insights into the potential trajectory of cancer in the coming years.
Key Trends Shaping the Future of Cancer Care
1. The Rise of Personalized Medicine:
The era of one-size-fits-all cancer treatment is fading. Personalized medicine, driven by advancements in genomics, proteomics, and other "omics" technologies, is enabling physicians to tailor treatments to individual patients based on their unique genetic makeup and tumor characteristics. This approach holds immense promise for improving treatment efficacy, minimizing side effects, and potentially even preventing cancer in high-risk individuals.
- Genomic Profiling: Next-generation sequencing (NGS) technologies are revolutionizing cancer diagnosis and treatment. Genomic profiling allows for the identification of specific genetic mutations within a tumor, providing crucial information for treatment selection and prognosis. This personalized approach enables doctors to choose the most effective therapies based on the specific genetic alterations driving the cancer.
- Immunotherapy: Immunotherapy harnesses the power of the body’s own immune system to fight cancer. Immune checkpoint inhibitors, CAR T-cell therapy, and other immunotherapy approaches are showing remarkable success in treating a range of cancers. These therapies are particularly promising for cancers that have become resistant to traditional treatments.
- Liquid Biopsies: Liquid biopsies, which analyze circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) in blood samples, offer a minimally invasive and more frequent way to monitor cancer progression and treatment response. They can detect cancer recurrence earlier than traditional imaging methods, allowing for timely intervention and potentially improving patient outcomes.
2. Focus on Early Detection and Prevention:
Early detection remains a cornerstone of successful cancer treatment. Advancements in screening technologies and the development of novel biomarkers are leading to more accurate and sensitive methods for detecting cancer at its earliest stages. These developments are crucial for improving patient outcomes and reducing cancer mortality.
- AI-powered Screening: Artificial intelligence (AI) is playing a transformative role in cancer screening. AI algorithms can analyze medical images, such as mammograms and colonoscopies, with greater accuracy and speed than human radiologists. This technology is enabling faster and more efficient screening, leading to earlier detection and potentially better outcomes.
- Liquid Biopsy Screening: Liquid biopsies are not only useful for monitoring cancer progression but also hold promise for early detection. Researchers are exploring the use of ctDNA analysis to screen for cancer in asymptomatic individuals, potentially leading to earlier diagnoses and improved survival rates.
- Lifestyle Interventions: Lifestyle factors, such as smoking, unhealthy diet, and lack of physical activity, are major contributors to cancer risk. Public health initiatives promoting healthy lifestyle choices are crucial for preventing cancer and reducing the burden of the disease.
3. Advancements in Cancer Treatment:
The landscape of cancer treatment is constantly evolving, with new drugs, therapies, and treatment modalities emerging regularly. These advancements are leading to more effective and targeted treatments, with fewer side effects and improved patient quality of life.
- Targeted Therapies: Targeted therapies focus on specific molecular pathways involved in cancer growth and development. These therapies are highly effective in treating certain types of cancer, such as leukemia and breast cancer, and are associated with fewer side effects than traditional chemotherapy.
- Combination Therapies: Combining different treatment modalities, such as chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and immunotherapy, is becoming increasingly common. This approach can enhance treatment efficacy, target different aspects of cancer development, and potentially overcome drug resistance.
- Precision Radiation Therapy: Advancements in radiation therapy, such as stereotactic radiosurgery and intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT), allow for more precise delivery of radiation to tumors while minimizing damage to surrounding healthy tissues. This precision approach is improving treatment outcomes and reducing side effects.
4. Improved Access to Care and Patient Empowerment:
Ensuring equitable access to quality cancer care is paramount. Efforts to expand access to screening, diagnosis, and treatment are crucial for reducing cancer disparities and improving patient outcomes. Furthermore, empowering patients to actively participate in their own care is essential for improving treatment adherence, promoting patient well-being, and enhancing overall outcomes.
- Telemedicine and Remote Monitoring: Telemedicine is bridging geographical barriers and expanding access to specialized cancer care. Remote monitoring technologies allow for more frequent and convenient checkups, improving patient engagement and potentially leading to earlier detection of treatment complications.
- Patient Education and Support: Providing patients with comprehensive information about their diagnosis, treatment options, and potential side effects is essential for informed decision-making and improved patient outcomes. Support groups and online communities offer valuable resources for patients to connect with others facing similar challenges and receive emotional and practical support.
5. Focus on Cancer Survivorship:
Cancer survivorship is increasingly recognized as a crucial aspect of cancer care. Efforts are underway to improve the quality of life for cancer survivors, addressing physical, emotional, and psychosocial challenges they may face.
- Post-treatment Surveillance: Regular follow-up care, including screenings and monitoring for potential complications, is essential for detecting cancer recurrence early and improving patient outcomes.
- Addressing Long-Term Side Effects: Cancer treatment can have long-term side effects, such as fatigue, cognitive impairment, and cardiovascular problems. Providing support and resources to address these challenges is crucial for improving the quality of life for cancer survivors.
- Support for Psychological and Social Well-being: Cancer diagnosis and treatment can have a significant impact on mental health and social well-being. Providing access to psychological counseling, support groups, and other resources can help cancer survivors cope with the emotional and social challenges they face.
Related Searches:
1. Cancer Incidence and Mortality Trends:
Analyzing cancer incidence and mortality trends provides valuable insights into the burden of cancer and the effectiveness of prevention and treatment strategies. Globally, cancer incidence is increasing, driven by factors such as population growth, aging, and lifestyle changes. However, mortality rates are declining in many countries, indicating progress in early detection, treatment, and cancer control programs.
2. Cancer Prevention Strategies:
Cancer prevention strategies aim to reduce the risk of developing cancer through lifestyle modifications, vaccination, and other interventions. Public health campaigns promoting healthy lifestyle choices, such as quitting smoking, maintaining a healthy weight, and engaging in regular physical activity, are crucial for reducing cancer risk. Vaccination against human papillomavirus (HPV) is highly effective in preventing cervical cancer and other HPV-related cancers.
3. Cancer Screening Guidelines:
Cancer screening guidelines recommend specific tests and intervals for detecting cancer at early stages, when treatment is most likely to be successful. These guidelines are based on scientific evidence and aim to balance the benefits of early detection with the potential risks and costs associated with screening. Regular screening for common cancers, such as breast, cervical, colorectal, and prostate cancer, is essential for improving patient outcomes.
4. Cancer Treatment Options:
The range of cancer treatment options available to patients has expanded significantly in recent years, offering more targeted and effective therapies with fewer side effects. Treatment options include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, immunotherapy, and targeted therapies. The specific treatment approach chosen for a patient depends on the type and stage of cancer, as well as the patient’s overall health and preferences.
5. Cancer Research Advancements:
Cancer research is a rapidly evolving field, with ongoing efforts to develop new and more effective treatments, improve diagnosis and screening, and understand the underlying causes of cancer. Clinical trials play a crucial role in testing new therapies and evaluating their safety and efficacy. Advances in genomics, immunotherapy, and other emerging technologies are leading to significant breakthroughs in cancer research.
6. Cancer Support Services:
Cancer support services provide emotional, practical, and financial assistance to patients and their families during their cancer journey. These services may include counseling, support groups, transportation assistance, and financial aid. Support services play a vital role in improving patient well-being and helping them cope with the challenges of cancer.
7. Cancer Disparities:
Cancer disparities refer to differences in cancer incidence, mortality, and access to care among different populations. These disparities are often influenced by factors such as race, ethnicity, socioeconomic status, and geographic location. Addressing cancer disparities is crucial for ensuring equitable access to quality cancer care and improving health outcomes for all populations.
8. Cancer Policy and Advocacy:
Cancer policy and advocacy focus on shaping policies and promoting initiatives to improve cancer prevention, diagnosis, treatment, and support services. Advocacy organizations play a crucial role in raising awareness, advocating for increased funding for cancer research, and ensuring access to quality cancer care for all.
FAQs about Cancer Trends 2025
1. Will cancer be cured by 2025?
While a cure for all types of cancer is not expected by 2025, significant progress is being made in treating and preventing cancer. Emerging technologies and innovative therapies are offering hope for better outcomes and potentially even cures for certain types of cancer. However, a universal cure remains a long-term goal for cancer research.
2. How will technology impact cancer care in 2025?
Technology is poised to revolutionize cancer care in the coming years. Advancements in genomics, AI, and other fields will lead to more personalized treatments, earlier detection, and improved patient outcomes. AI-powered screening tools, liquid biopsies, and remote monitoring technologies are expected to play a significant role in enhancing cancer care.
3. What are the most promising cancer treatments in development?
Immunotherapy, targeted therapies, and combination therapies are among the most promising cancer treatments in development. These approaches offer the potential to target specific cancer cells, minimize side effects, and overcome drug resistance. Clinical trials are ongoing to evaluate the effectiveness and safety of these therapies.
4. What can I do to reduce my risk of cancer?
Lifestyle choices play a significant role in cancer risk. Maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular physical activity, avoiding smoking, limiting alcohol consumption, and consuming a balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables can help reduce the risk of cancer. Regular cancer screenings are also crucial for early detection and improved outcomes.
5. What are the challenges facing cancer research and treatment?
Challenges facing cancer research and treatment include the need for continued funding, the development of effective therapies for difficult-to-treat cancers, and ensuring equitable access to quality cancer care for all populations. Overcoming these challenges requires a concerted effort from researchers, healthcare providers, policymakers, and the public.
Tips for Cancer Prevention and Early Detection
- Maintain a healthy weight: Obesity is a major risk factor for several types of cancer. Maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular physical activity can significantly reduce cancer risk.
- Quit smoking: Smoking is a leading cause of lung cancer and other cancers. Quitting smoking is one of the most effective ways to reduce cancer risk.
- Limit alcohol consumption: Excessive alcohol consumption is linked to an increased risk of several cancers, including breast, liver, and colorectal cancer. Limiting alcohol intake can reduce cancer risk.
- Get vaccinated: Vaccines are available to protect against HPV, which is a major cause of cervical cancer and other cancers. Vaccination is highly effective in preventing these cancers.
- Follow cancer screening guidelines: Regular cancer screenings are essential for early detection and improved outcomes. Follow recommended screening guidelines for breast, cervical, colorectal, prostate, and other cancers.
- Be aware of family history: Certain types of cancer have a strong family history component. If you have a family history of cancer, talk to your doctor about your risk factors and appropriate screening recommendations.
Conclusion
Cancer trends 2025 point towards a future where cancer care is more personalized, preventative, and effective than ever before. Advancements in technology, research, and treatment modalities are transforming the way we understand, diagnose, and treat cancer. While challenges remain, the ongoing commitment to innovation and patient-centered care offers hope for a future where cancer is no longer a death sentence but a manageable disease. By embracing healthy lifestyle choices, adhering to screening guidelines, and staying informed about the latest developments in cancer research, we can all contribute to a future where cancer is defeated.



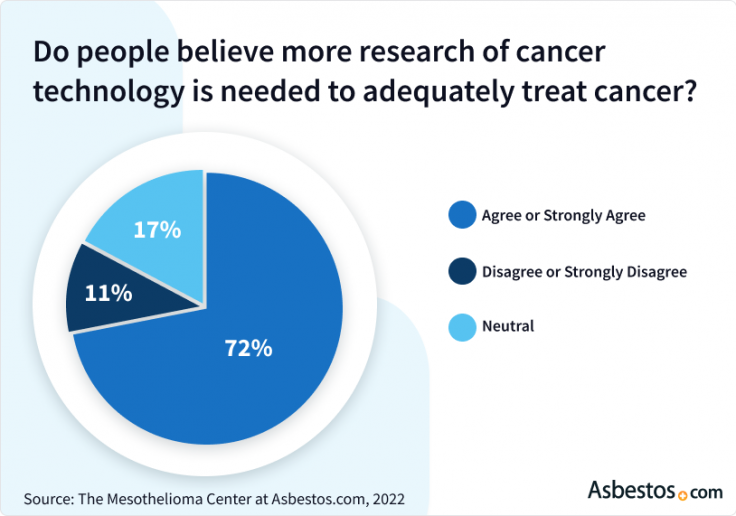



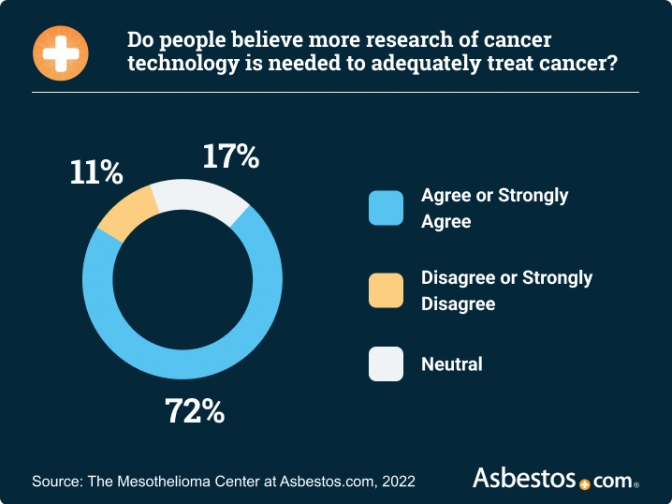
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Cancer Trends 2025: A Glimpse into the Future of Cancer Care. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!