California Population Trends 2025: A Comprehensive Look At The Golden State’s Future
California Population Trends 2025: A Comprehensive Look at the Golden State’s Future
California Population Trends 2025: A Comprehensive Look at the Golden State’s Future
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to California Population Trends 2025: A Comprehensive Look at the Golden State’s Future. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
California Population Trends 2025: A Comprehensive Look at the Golden State’s Future

California, the Golden State, has long been a beacon of opportunity and growth, attracting millions seeking a better life. However, in recent years, California population trends have taken a surprising turn, with a shift away from the traditional pattern of steady growth. Understanding these trends is crucial, as they have far-reaching implications for the state’s economy, infrastructure, and social fabric. This article delves into the projected population changes, exploring the key factors driving these shifts and their potential consequences for California’s future.
Projected Population Growth: A Slowing Pace
While California’s population has historically been on an upward trajectory, projections for 2025 suggest a significant slowdown in growth. According to the California Department of Finance, the state’s population is expected to reach approximately 40.6 million by 2025, a mere 1.7% increase from 2020. This contrasts sharply with the average annual growth rate of 1.5% seen between 1990 and 2010. This slowing growth can be attributed to a confluence of factors:
- Declining Birth Rates: California’s birth rate has been steadily declining for several decades, falling below the replacement rate needed to sustain population growth. This trend is partly due to factors like delayed marriage and childbearing, coupled with a growing preference for smaller families.
- High Cost of Living: California’s notoriously high cost of living, particularly in major cities, has become a significant deterrent for many individuals and families. The soaring housing costs, coupled with rising expenses for healthcare, education, and utilities, make it challenging for many to make ends meet.
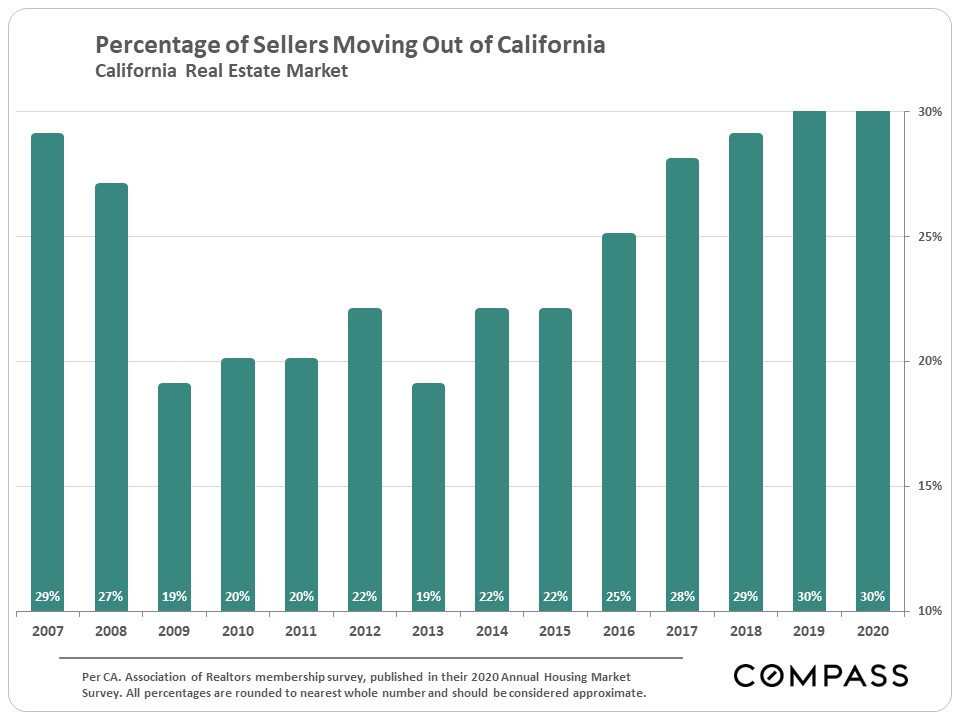
- Outmigration: California has witnessed a net outmigration in recent years, with more people leaving the state than moving in. This trend is driven by a combination of factors, including the high cost of living, limited job opportunities in certain sectors, and concerns about social and political issues.
Regional Variations in Population Trends:
While the state as a whole experiences a slowing growth rate, California population trends exhibit significant regional variations. Some areas continue to experience growth, while others face population decline.
- Coastal Cities: Slowing Growth: Major coastal cities like Los Angeles, San Francisco, and San Diego, once magnets for population growth, are now seeing their growth rates slow down. The high cost of living and limited housing affordability are major factors contributing to this trend.
- Inland Regions: Stagnant or Declining: Inland regions, including the Central Valley and the Inland Empire, are experiencing stagnant or even declining populations. These areas face challenges related to economic opportunity, limited access to quality education and healthcare, and environmental concerns.
- Rural Areas: Population Decline: Rural areas in California, particularly those in the north and east, have witnessed a significant decline in population. This is primarily due to factors like limited job opportunities, declining agricultural industries, and a lack of access to essential services.
Implications of Shifting Population Trends:
The changing California population trends have far-reaching implications for the state’s future, impacting its economy, infrastructure, and social fabric.
- Economic Impact: The slowing population growth can impact the state’s economy in several ways. A smaller workforce can lead to labor shortages in key sectors, potentially affecting economic growth. Additionally, declining populations in certain regions can strain local economies, leading to a decline in tax revenue and reduced funding for public services.
- Infrastructure Strain: The changing demographics can put a strain on existing infrastructure, particularly in areas with declining populations. This can lead to underutilized infrastructure, higher maintenance costs, and reduced efficiency.
- Social and Political Impact: The shifts in population can have significant social and political consequences. Aging populations can lead to increased demand for healthcare and social services, while declining birth rates can impact future generations and the workforce. These changes can also influence political dynamics, as different regions with varying demographics may have different priorities and needs.
Related Searches:
California population trends are a complex and multifaceted issue, prompting a range of related searches. Here’s a closer look at some of the key areas of interest:
1. California Population Projections:
- Population by Age: Understanding the age distribution of California’s population is crucial for planning for future healthcare needs, social services, and workforce requirements. Projections show an increasing share of the population aged 65 and older, indicating a growing need for senior care and retirement services.
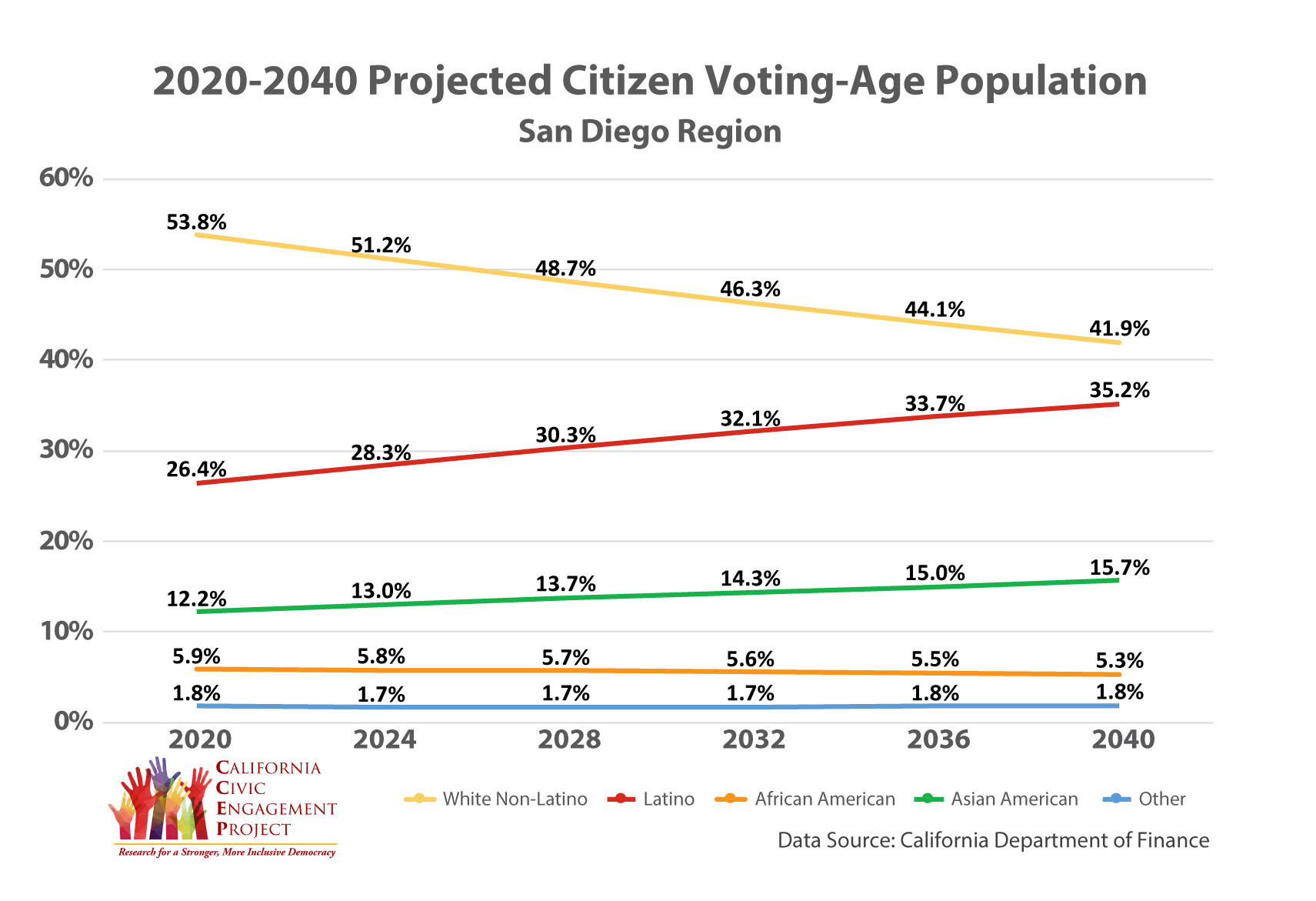
- Population by Race and Ethnicity: California is a diverse state, and its population projections highlight the growing influence of minority groups. Projections suggest that the Hispanic population will continue to grow significantly, while the Asian population will also experience substantial growth.
- Population by County: Regional variations in population growth are significant. Understanding county-level population projections is essential for local planning and resource allocation.
2. California Housing Market:
- Housing Affordability: The high cost of housing is a major factor driving outmigration and slowing population growth in California. Understanding the affordability crisis and its impact on different demographics is crucial for policymakers and housing developers.
- Housing Supply: The limited housing supply, particularly in major urban centers, is a key contributor to the affordability crisis. Analyzing the factors affecting housing construction and affordability is essential for addressing the housing shortage.
- Housing Policy: California has implemented various housing policies to address the affordability crisis, including zoning reforms, tax incentives, and affordable housing programs. Evaluating the effectiveness of these policies and exploring alternative solutions is crucial for ensuring adequate and affordable housing for all.
3. California Economy:
- Economic Growth: The state’s economic growth is closely tied to its population dynamics. Understanding the impact of slowing population growth on key sectors like technology, healthcare, and tourism is essential for policymakers and businesses.
- Job Market: The evolving demographics can influence the job market, creating new opportunities while also potentially leading to labor shortages in certain industries. Analyzing the changing job landscape and its implications for workforce development is crucial.
- Tax Revenue: Population changes can affect tax revenue, influencing the state’s ability to fund public services. Understanding the impact of population shifts on tax revenue and exploring alternative revenue sources is crucial for maintaining essential services.
4. California Infrastructure:
- Transportation: California’s transportation infrastructure faces challenges related to population growth and urbanization. Understanding the impact of population trends on transportation systems and exploring solutions for congestion and accessibility is essential for maintaining efficient movement of people and goods.
- Water Resources: California faces significant water challenges, exacerbated by population growth and climate change. Understanding the impact of population trends on water demand and exploring sustainable water management strategies is crucial for ensuring adequate water resources for the future.
- Energy Consumption: Population growth can lead to increased energy consumption. Understanding the impact of population trends on energy demand and exploring alternative energy sources is crucial for meeting the state’s energy needs while reducing environmental impact.
5. California Education:
- School Enrollment: Changing demographics can affect school enrollment, impacting school funding and resource allocation. Understanding the impact of population trends on school enrollment and exploring strategies for ensuring access to quality education for all students is crucial.
- Higher Education: California’s higher education system plays a vital role in attracting and retaining skilled workers. Understanding the impact of population trends on higher education enrollment and funding is essential for ensuring access to quality education and supporting economic growth.
- Teacher Shortages: The changing demographics and potential labor shortages can affect the availability of qualified teachers. Understanding the challenges of teacher recruitment and retention and exploring solutions for addressing teacher shortages is crucial for ensuring quality education for all students.
6. California Healthcare:
- Healthcare Demand: An aging population can lead to increased demand for healthcare services. Understanding the impact of population trends on healthcare demand and exploring strategies for ensuring access to quality healthcare for all is crucial.
- Healthcare Costs: Rising healthcare costs are a major concern in California, particularly for seniors and low-income individuals. Understanding the factors driving healthcare costs and exploring solutions for affordability is crucial for ensuring access to essential healthcare services.
- Healthcare Workforce: The aging population and increasing demand for healthcare services can lead to shortages in the healthcare workforce. Understanding the challenges of attracting and retaining healthcare professionals and exploring solutions for addressing these shortages is crucial for ensuring quality healthcare for all.
7. California Environment:
- Climate Change: California is particularly vulnerable to the effects of climate change, including rising sea levels, more frequent and intense wildfires, and drought. Understanding the impact of population trends on climate change adaptation and mitigation is crucial for protecting the environment and ensuring the well-being of residents.
- Environmental Sustainability: Population growth can strain natural resources and increase environmental pollution. Understanding the impact of population trends on environmental sustainability and exploring solutions for reducing environmental impact is crucial for protecting the state’s natural beauty and resources.
- Conservation Efforts: California has implemented various conservation programs to protect its natural resources. Understanding the impact of population trends on conservation efforts and exploring strategies for ensuring the effectiveness of these programs is crucial for preserving the state’s biodiversity and natural beauty.
8. California Social Issues:
- Social Inequality: California faces significant challenges related to social inequality, including income disparities, access to healthcare, and educational opportunities. Understanding the impact of population trends on social inequality and exploring solutions for promoting social justice and equity is crucial for building a more inclusive and equitable society.
- Public Safety: The changing demographics can impact public safety, requiring adjustments in policing and crime prevention strategies. Understanding the impact of population trends on public safety and exploring solutions for ensuring the safety and security of all residents is crucial.
- Community Development: The shifts in population can impact community development, requiring adjustments in planning and resource allocation. Understanding the impact of population trends on community development and exploring strategies for creating vibrant and thriving communities is crucial for ensuring the well-being of all residents.
FAQs:
Q: Will California’s population continue to decline?
A: It’s difficult to predict with certainty whether California’s population will continue to decline. While projections suggest a slowdown in growth, the state’s future population trajectory will depend on various factors, including economic conditions, housing affordability, and social and political policies.
Q: What is the impact of outmigration on California’s economy?
A: Outmigration can have both positive and negative impacts on California’s economy. While it can alleviate pressure on housing and resources, it can also lead to a decline in the workforce, potentially impacting economic growth.
Q: How will California address the challenges posed by an aging population?
A: California is taking steps to address the challenges posed by an aging population, including expanding healthcare services, promoting senior housing options, and supporting programs that promote active aging.
Q: What are the implications of declining birth rates for California’s future?
A: Declining birth rates can have long-term implications for California’s future, potentially impacting the workforce, tax revenue, and social services. It’s crucial for the state to address these challenges and ensure a sustainable future for its residents.
Tips for Navigating California’s Population Trends:
- Stay Informed: Keeping abreast of the latest California population trends is crucial for individuals, businesses, and policymakers. Stay informed about projections, demographic changes, and the factors driving these trends.
- Adapt to Change: As California population trends evolve, individuals and businesses need to adapt to changing demographics and market conditions. This may involve adjusting business strategies, seeking new opportunities, and investing in skills development.
- Support Sustainable Solutions: The challenges posed by California population trends require sustainable solutions. Support policies and initiatives that promote affordable housing, sustainable infrastructure, and environmental conservation.
- Advocate for Equity: The changing demographics highlight the need for greater equity and social justice. Advocate for policies that promote equal opportunities and access to resources for all Californians, regardless of background or location.
Conclusion:
California population trends are a complex and dynamic issue with far-reaching implications for the state’s future. Understanding the factors driving these trends, their potential consequences, and the strategies for navigating these changes is crucial for ensuring a prosperous and sustainable future for California. By embracing innovation, promoting equity, and investing in sustainable solutions, the Golden State can continue to thrive in the face of changing demographics and navigate the challenges and opportunities of its evolving population landscape.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into California Population Trends 2025: A Comprehensive Look at the Golden State’s Future. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!